
Abb.: RSS und seine Family (Hindi: संघ परिवार)
[Bildquelle: http://www.spandanfeatures.com/increasing-steps-of-rss-in-the-service-of-the-nation/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-13. -- Fair use]
Zitierweise | cite as: Payer, Margarete <1942 - >: Hindunationalismus - Hindutva : Organisationen. -- Fassung vom 2018-03-18. -- URL: http://www.payer.de/hindunationalismus/organisationen.htm
Erstmals hier publiziert:
Überarbeitungen:
©opyright: Creative Commons Lizenz (Namensnennung, keine kommerzielle Nutzung, share alike)
Dieser Text ist Teil der Abteilung Modernes Indien von Tüpfli's Global Village Library

Abb.: RSS und seine Family (Hindi: संघ परिवार)
[Bildquelle:
http://www.spandanfeatures.com/increasing-steps-of-rss-in-the-service-of-the-nation/.
-- Zugriff am 2018-02-13. -- Fair use]
| Name | Sangh Parivar - Hindi: संघ परिवार |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Dachverband |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Mitglieder | |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | --- |
| Webpräsenz | --- |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sangh_Parivar. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
Die wichtigste -- und gefährlichste -- Form von organisiertem Hinduismus, der den Religionsfrieden in Indien stört und zerstört, ist der Sangh Parivar (Hindi: संघ परिवार), die "Familie des Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS) (Hindi: राष्ट्रीय स्वयंसेवक संघ)". Diese "Familie" umfasst viele Organisationen: die meisten sind Zweigorganisationen, die eine gewisse Autonomie in der Theorie haben, aber den Leitern des Sangh berichten müssen. Andere vertreten die gleiche Ideologie und arbeiten mit dem Sangh eng zusammen oder sind durch ihren Gründer verbunden mit dem Sangh (z. B. Hindu Yuva Vahini -- Hindi: हिन्दू युवा वाहिनी). Mit den vielen Organisationen erreicht man praktisch alle Völker, Bevölkerungsschichten und Menschen in jedem Lebensalter in Indien und Inder im Ausland. Der RSS ist weitgehend verantwortlich für die heutige Lage Indiens: der Alternative Nobelpreisträger Colin Gonsalves (1952 - ), der als Menschenrechtsanwalt vor dem Obersten Gerichtshof es z.B. geschafft hat, dass Soldaten zum erstem Mal für Morde an Zivilpersonen verurteilt wurden, sieht die Entwicklung in Indien so:
"Für Arme ist es viel schlimmer geworden! Hunger und Mangelernährung sind verbreitet: 700 Millionen gehen jeden Tag hungrig ins Bett. Die Hälfte der Frauen und Kinder sind unterernährt und schwach... Einer der größten Fehler von Ökonomen ist es, zu glauben, dass die Menschen besser leben, weil die Wirtschaft wächst. Die Sozialausgaben sind radikal gekürzt worden. Da sickert kein Wohlstand nach unten durch, wie in sozialen Systemen. Indien ist ein besserer Ort nur für Industrielle, Kapitalisten und Reiche geworden... Die indische Politik hat die Idee übernommen, der Staat müsse nicht für Wohnungen, Essen und Bildung bezahlen. Das mache alles der Markt. Aber der macht es nicht... In Indien breitet sich extremer Nationalismus aus. Die Regierungspartei von Ministerpräsident Narendra Modi baut nur auf einer Idee auf: Dass Hindus die besseren Menschen sind. Unsere Nationalisten sind um ein vielfaches hasserfüllter als etwa Marine Le Pen. Vor Jahren habe ich gesagt, dass wir uns auf den Faschismus zubewegen. Damit hatte ich Recht. Wir sind mittendrin im Faschismus...Faschismus. Menschen haben das Sagen, die an die Überlegenheit einer bestimmten Rasse glauben. Die finden, Muslime gehören in die Schranken gewiesen, im Zweifel auch mit Gewalt. Wir erleben die Ghettoisierung von Muslimen. Im vergangenen Jahr haben militante Hindus vierzig Menschen gelyncht, weil sie Rindfleisch essen. Hitler, Mussolini, Franco werden verehrt. Die ganze Welt schaut weg, dabei sind wir die größte Demokratie der Welt." [Colin Gonsalves interviewt von Jonas Schaible: Menschenrechtler Colin Gonsalves "Die ganze Welt schaut weg". - 2017-12-07. - In T-Online. - http://www.t-online.de/nachrichten/ausland/id_82833974/alternativer-nobelpreistraeger-in-indien-droht-faschismus.html . - Zugriff am 2017-12-11]

Abb.: Colin Gonsalves (1952 - ), 2006
[Bildquelle: Human Rights Law Network/Wikimedia. --
CC BY-SA 4.0]
Madhu Kishwar [मधु पूर्णिमा किश्वर] über die Einstellung des Sangh Parivar [Hindi: संघ परिवार] zu Muslimen:
"Let us look closely at the grievance list of the Sangh Parivar [Hindi: संघ परिवार] given below. It was synthesised from themes frequently repeated in a variety of its media efforts, including its political organ, The Organiser, its propaganda leaflets, and the recorded cassettes of its celebrated pracharaks (Hindi: प्रचारक).
- Muslims are traitors because they forced the Partition of India. To quote a VHP [Vishva Hindu Parishad -- Sanskrit/Hindi: विश्व हिंदू परिषद] propaganda cassette,” Those who severed both the arms of Mother India...For those hypocrites there is no place here. This Hindustan is not theirs...”
- Since the vast majority of Hindus were driven out of Pakistan, and later even from Bangladesh, the Congress party led by Mahatma Gandhi [Gujarati: મોહનદાસ કરમચંદ ગાંધી, १८६९ - १९४८] betrayed the nation by insisting that Muslims should not likewise be driven out of India.
- Muslims living in India are not loyal to this country and harbour pro-Pakistan sentiments.
- Muslims put their religion above the nation, and the Koran [Arabisch: القرآن] above the Constitution. The refusal of Muslims to accept a common civil code, and their insistence on being governed by their religious personal laws, are touted as proofs of their lack of nationalist spirit.
- Muslims are inherently intolerant and obscurantist and do not allow even reasonable criticism of Islam.
- Pakistan is constantly attempting to destabilise India by fanning secessionist movements in Punjab [Panjabi: ਪੰਜਾਬ] and Kashmir [Urdu: کشمیر]. Muslims of India are willing pawns in the games played by Pakistani rulers.
- The Congress party has followed a policy of appeasing the Muslims by submitting even to their unreasonable and anti-national demands. Muslims behave like “a virtual nation within a nation” (Organiser, April, 1992); a people who assert their right to be above the law of the land. The passing of the Muslim Women's (protection) Act under pressure from Muslim fundamentalists, thereby putting Muslims beyond the pale of some laws governing other citizens, is cited as one of the examples of this appeasement. Other examples cited are the special status given to minority institutions and the provisions allowing the Muslim majority state of Jammu and Kashmir [Kashmiri: जोम त् कशीर / جۄم تہٕ کٔشِیر] separate provisions in the Constitution and a few separate personal laws.
- Muslim invaders and rulers who persecuted Hindus, such as Aurangzeb [1618 - 1707] [Persisch: محي الدين محمد )] or Mahmud of Ghazni [971 - 1030] [Persisch محمود غزنوی ], are not criticised in the name of secularism while Hindus are constantly expected to criticise and suppress their own heritage to prove that they are modern and secular. One of the Sangh Parivar's war cries is: Garv se kaho ham Hindu hain [गर्व से कहो हम हिंदू हैं]. (Say with pride, we are Hindus.) They are resentful that Muslims continue to honour even those rulers who persecuted Hindus. This is cited as another proof that Muslims are anti-national.
- The large scale one-way flow of Muslim Bangladeshi illegal immigrants into India is jeopardising the security of India and putting a great strain on the Indian economy, as well as upsetting the demographic balance. They accuse Muslims of using their electoral clout with the Congress in order to prevent strong steps from being taken to stop the continuing persecution of Hindus in Bangladesh which is forcing a large number of them to flee to India.
- The mullahs do not allow Muslims to accept birth control measures. This, together with the right of Muslim men to have four wives encourages a higher birth rate creating the danger of the Hindus being swamped by the Muslims.
- Muslim leaders try to dictate on foreign policy matters to the Indian government. For example, they succeeded for a long time in keeping India from having full diplomatic relations with Israel and making India tilt in favour of Palestine and other Arab nations which are seen as inherently hostile to India because they are Islamic countries.
- India is being surrounded by hostile and troublesome Muslim nations, including Pakistan, Bangladesh, Malaysia, Indonesia, Afghanistan, the Middle Eastern and Gulf States, and the new Muslim States which have emerged after the breakdown of the Soviet Union. They are all threats to the security of India The supposed extra-territorial loyalty of Indian Muslims adds to the threat as their presence amounts to having an enemy within."
[Quelle: Kishwar, Madhu [मधु पूर्णिमा किश्वर] <1951 - >: Religion at the service of nationalism. -- In: Manushi. -- No. 76 (1993-05/06). -- S. 6ff. -- Online: https://archive.org/details/ReligionAtTheServiceOfNationalism. -- Zugriff am 2018-03-14. -- CC BY-NC-ND 4.0]
Der Sangh Parivar -- die Familie des Sangh <RSS> -- umfasst viele Organisationen des Hindunationalismus:
[Hauptquelle der Übersicht: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sangh_Parivar#Sangh_Parivar_members. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-16]
| Name | Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS) - Hindi: राष्ट्रीय स्वयंसेवक संघ - आर० एस० एस० |
|---|---|
| Funktion | rechtsradikale, hindunationalistische, paramilitärische Freiwilligenorganisation |
| Präsident 2018 | Mohan Madhukar Bhagwat (Maratihi: मोहन मधुकर भागवत, 1950 - ) |
| Mitglieder | 5 - 6 Millionen |
| Gegründet | 1925-09-27 |
| Hauptquartier | Nagpur (Marathi: नागपूर) |
| Mutterorganisation | Sangh Parivar - Hindi: संघ परिवार |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.rss.org. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-18 |
| Wikipedia | https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rashtriya_Swayamsevak_Sangh / https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rashtriya_Swayamsevak_Sangh. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
die einflussreichste Organisation des Sangh Parivar.
[Ausführliche Beschreibung s. RSS in Wort (Selbstdarstellung)]
1.1.1. All Jammu and Kashmir Praja Parishad [Hindi: प्रजा परिषद], literally, "People's Council", a political party active in Jammu [Hindi: जम्मू] from 1947 to 1963.
| Name | All Jammu and Kashmir Praja Parishad -- Hindi: प्रजा परिषद |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Politische Partei in Jammu [Hindi: जम्मू] from 1947 to 1963 |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | erloschen |
| Gegründet | 1947 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | RSS |
| Webpräsenz | --- |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jammu_Praja_Parishad. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
Gegründet 1947-11 vom RSS Aktivisten Balraj Madhok (Hindi: बलराज मधोक, 1920 – 2016)
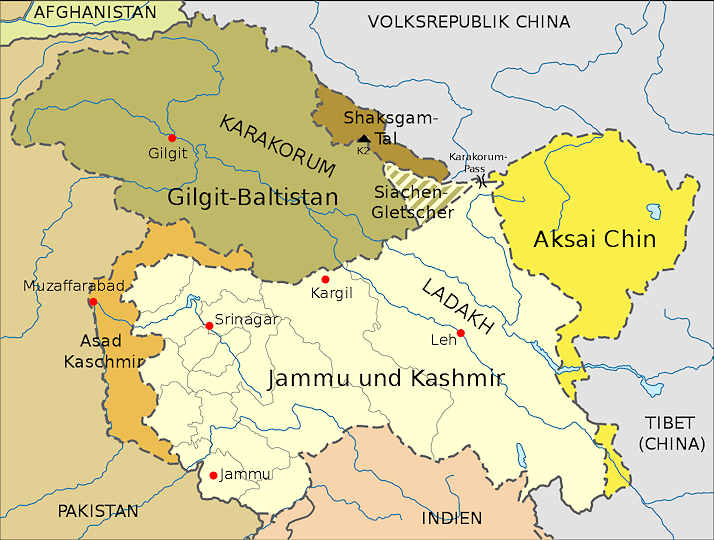
Abb.:
[Bildquelle: Furfur/Wikimedia. --
CC BY-SA 4.0]
1.1.2. Bharatiya Jana Sangh [Hindi: भारतीय जनसंघ], literally, "Indian People's Association" a political party that existed from 1951 to 1974.
| Name | Bharatiya Jana Sangh -- Hindi: भारतीय जनसंघ -- Indian People's Association |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Politische Partei 1951 - 1977 |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | erloschen |
| Gegründet | 1951 |
| Hauptquartier | Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | RSS |
| Webpräsenz | --- |
| Wikipedia | https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bharatiya_Jana_Sangh / https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bharatiya_Jana_Sangh. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
1974 aufgegangen in: Bharatiya Lok Dal -- Hindi: भारतीय लोक दल -- Indian Peoples' Party

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP, "Indische Volkspartei") - Hindi: भारतीय जनता पार्टी -- Indian People's Party |
|---|---|
| Funktion | politischer Arm des Sangh Parivar (Hindi: संघ परिवार). |
| Präsident 2018 | Amit Shah (Marathi: अमित शाह, 1964 - ) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | über 100 Millionen |
| Gegründet | Die Partei ist 1980-12 nach einer Wahlniederlage hervorgegangen aus der Partei Bharatiya Jana Sangh (Hindi: भारतीय जनसंघ), gegründet 1951 übergegangen 1977 in die Janata Party (Hindi: जनता पार्टी). |
| Hauptquartier | Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | Sangh Parivar - Hindi: संघ परिवार, RSS |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.bjp.org -- Zugriff am 2018-02-18 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCrwE8kVqtIUVUzKui2WVpuQ. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/bjp4india?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bharatiya_Janata_Party / https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bharatiya_Janata_Party. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) [Hindi: भारतीय जनता पार्टी], Indian People's Party (100 million, March 2015)

Abb.: BJP Manifesto for 2014 Lok Sabha Elections
[Bildquelle: Narendra Modi. --
https://www.flickr.com/photos/92359345@N07/13970363996. -- Zugriff am
2018-02-13. --
CC BY-SA 2.0]
Das Parteisymbol ist die Lotosblume.
Die Parteifarbe ist Safran-Orange, um eindeutig als hinduistische Partei erkannt zu werden.
Parteivorsitzender ist Amit Shah (Marathi: अमित शाह, 1964 - )
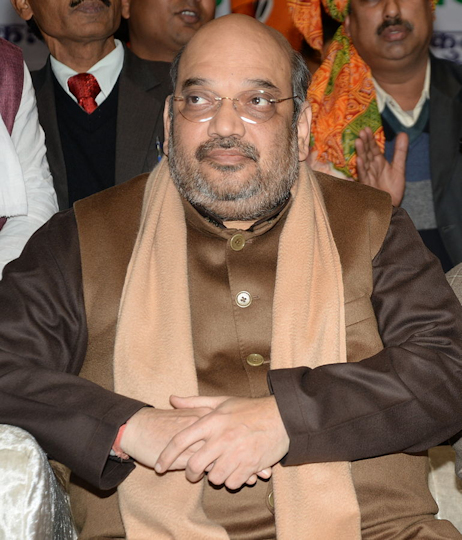

Abb.: Amit Shah (Marathi: अमित शाह, 1964 - ), 2015
[Bildquelle: Capankajsmilyo/Wikimedia. --
CC BY-SA 4.0]
Die BJP hat inzwischen über (Stand etwa 2015) 100 Millionen Mitglieder in einer straffen Organisation, nutzt sämtliche Angebote des Internet - insbesondere den Einsatz von Social media. Für die Wahlkämpfe der Partei werden die aktiven RSS-Anhänger zusätzlich eingesetzt.
Von 1998 bis 2004 konnte die Partei den indischen Premierminister stellen - Atal Bihari Vajpayee (Hindi: अटल बिहारी वाजपेयी, 1924 - ) - , nachdem es ihm gelungen war die National Democratic Alliance [NDA] (Hindi: राष्ट्रीय जनतांत्रिक गठबंधन - राजग) - ein Zusammenschluss mehrere Parteien - zu bilden.

Abb.: Atal Bihari Vajpayee (Hindi: अटल
बिहारी वाजपेयी, 1924 - )
[Bildquelle: LoC. -- Public domain]
In unterschiedlicher Zusammensetzung bildet die NDA heute unter Narendra Modi (Gujarati: નરેંદ્ર દામોદરદાસ મોદી; 1950 - ) die gesamtindische Regierung. Modi, ein Pracharak (Hindi: प्रचारक) im RSS, der ehemalige Chefminister von Gujarat (ગુજરાત), gewann bei den Parlamentswahlen 2014 die absolute Mehrheit der Parlamentssitze.
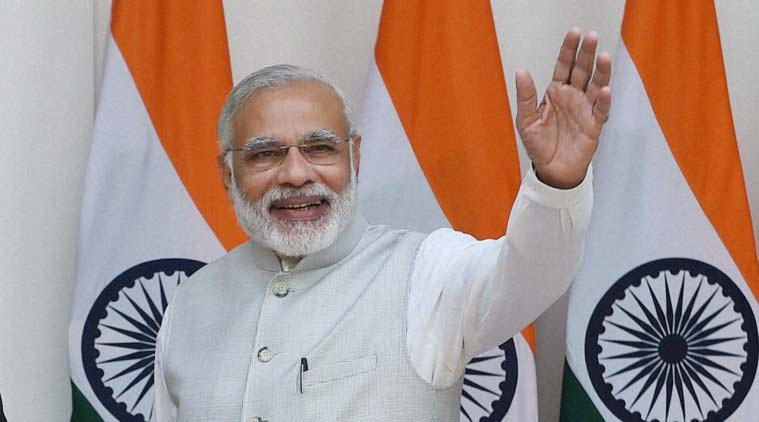

Abb.: Narendra Modi (Gujarati:
નરેંદ્ર દામોદરદાસ મોદી; 1950
- ), 2016
[Bildquelle: Jasveer10/Wikimedia. --
CC BY-SA 4.0]
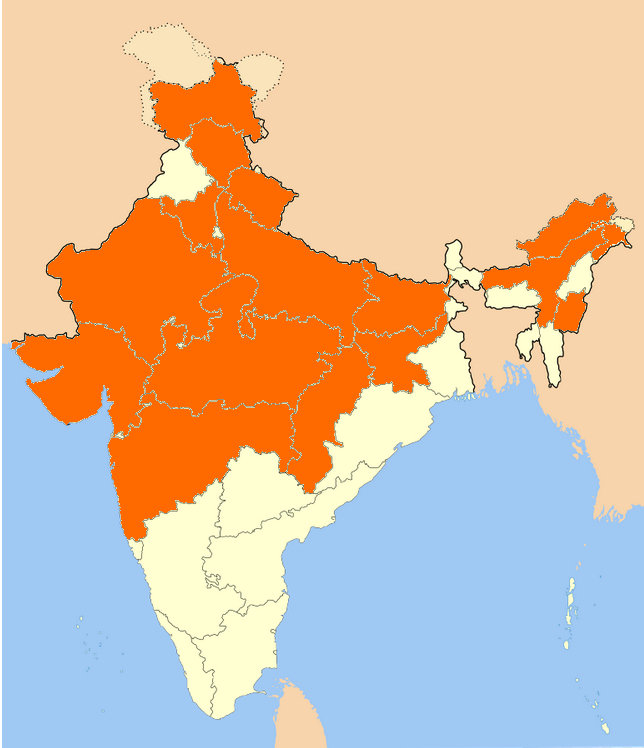
Abb.: Von BJP regierte Staaten 2017-12
[Kartenvorlage: Nichalp/Wikimedia. --
CC BY-SA 3.0]
Die Partei verpflichtet sich
"to nationalism and national integration, Democracy, Gandhian approach to socio-economic issues leading to the establishment of an egalitarian society free from exploitation`, Positive Secularism, that is, `Sarva Dharma Samabhav´[Sanskrit/Hindi: सर्वधर्म समभाव] and value-based politics. The party stands for decentralisation of economic and political power." [Article IV der "Constitution and Rules. - September, 1202. - http://www.bjp.org/images/pdf_2012_h/constitution_eng_jan_10_2013.pdf - Zugriff am 2016-08-23].
Die Partei bezeichnet sich als das prominenteste Mitglied der Familie des Sangh Parivar und ist aufgezogen ["nurtured] von der RSS.
"Like the RSS, the BJP is wedded to India´s unity and integrity, its intrinsic identity" [nämlich Identität als Hindus] "and the social strength, individual character and cultural uniqueness that have been the hallmark of this great country and its people for millenia." ... RSS ... "has no doubt about Hindu identity and culture being the mainstay of the Indian nation and of Indian society. This identity and this culture informs all Indians, irrespective of religious or denominational faith. To the RSS, all Indians, irrespective of religious background, notwithstanding their mode and place of worship, are equal." [http://org/en/about-the-party/history?u=bjp-history. - Zugriff am 2016-08-23]
Da vor allem indische Christen und indische Muslime die Hindu-Identität ablehnen, können sie als antiindisch verfolgt werden, sofern sie nicht bereit sind für eine Re-Konversion.
"Today BJP has emerged as a national party with strong right-wing tendencies which seriously threaten the existence of the minority communities of India. Confronting the minorities is central to BJP politics because they are seen as major obstacles to the realisation of the Hindu rashtra [Sanskrit/Hindi: हिन्दू राष्ट्र]. By minorities they mean, especially the Muslims, Christians, Communists, Dalits and Tribals." [s. Kuruvachira, J. : Politicisation of Hindu religion in postmodern India. - Jaipur [u.a.] : Rawat, 2008. - S. 3]
Um die Partei mit ihrer Hindutva-Ideologie bekannt zu machen, sind die verschiedenen Rath Yatras (Hindi: रथ यात्रा) wichtig: das sind traditionelle hinduistische Feste, bei denen auf einem Prozessionswagen das Bildnis eines Gottes - meistens Krishna [Sanskrit: कृष्ण] - durch einen Ort gezogen wird. Ab 1980 haben Politiker solche Rath Yatras eingesetzt, um die Massen der indischen Wähler zu mobilisieren. Der politisch wohl wirksamste Umzug war 1990 Ram Rath Yatra (Hindi: राम रथ यात्रा): mit einem weißen Toyota, der als Götterwagen hergerichtet war. Die Yatra ging von Somnath (સોમનાથ) durch viele indische Teilstaaten nach Ayodhya (अयोध्या) mit der Babri-Moschee (بابری مسجد), von der man behauptet, dass sie auf dem Platz eines indischen Tempels stände, der die Geburtsstätte Rams (राम) sei. Verantwortlich für Planung und Durchführung war Lal Krishna Advani (1927 - ) (Sindhi: لال کرشن اڈوانی), ein RSS Pracharak (Hindi: प्रचारक), der dreimal Präsident der BJP war. Ein wichtiger Helfer war Narendra Modi. [Ausführliche Beschreibung der Yatra und der Zerstörung der Moschee s. unten]
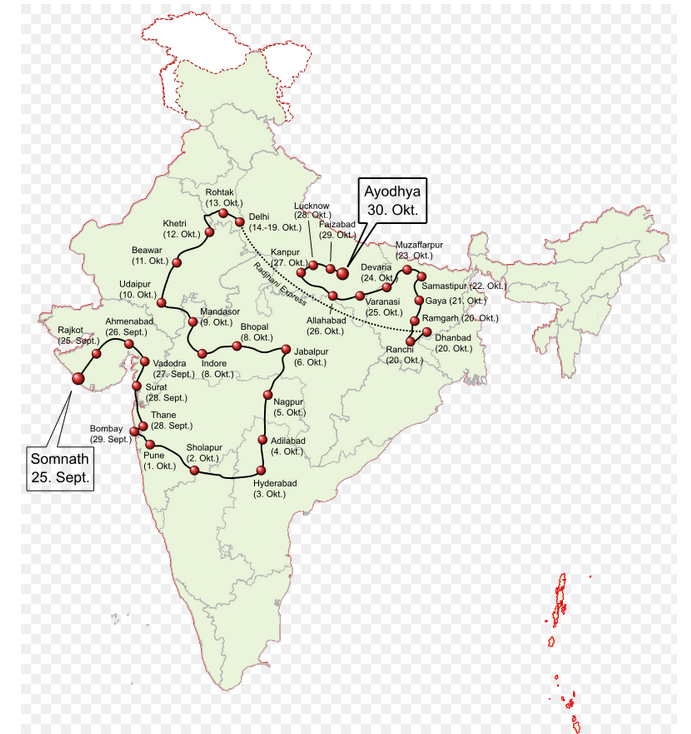
Abb.: Verlauf der Ram Rath Yatra (Hindi: राम रथ यात्रा) 1990-09-25 - 1990-10-30
Bildquelle: David Ludden / Furfur / Wikimedia. --
Creative
Commons Lizenz (BY - SA)
In einer Rede vor wichtigen Parteiführern betonte Modi, dass Nationalismus die Identität der BJP ist. Dabei verwies er auf die Tiranga Yatra (Hindi: तिरंगा यात्रा) von BJP Abgeordneten, die gerade stattfindet:
"Tiranga Yatra united India against forces who are trying to disturb social fabric" [zitiert in: Modi says nationalism is BJP´s identity; Cong calls remark `political deception´. -In: Hindustan Times.- Kindle ed. - 2016-08-24]
Bei dieser Veranstaltung wies der heutige Vorsitzende der BJP, Amit Shah (Marathi: अमित शाह, 1964 - ), darauf hin, dass die Partei mehr als 1000 MLAs [Member of Legislative Assembly], mehr als 300 MPs [Member of Parliament] und die Regierung in 13 Staaten hat
Während der Regierungsperiode von Atal Bihari Vajpayee (Hindi: अटल बिहारी वाजपेयी,1998-2004) haben die Angriffe auf Christen und Muslime deutlich zugenommen, wobei man davon ausgeht, dass die zuständigen Politiker bewusst nicht eingegriffen haben, um die Angriffe zu stoppen. Z. B. hat Lal Krishna Advani in seiner Zeit als Union Home Minister of India (1999-2004) nichts getan, um 2002 (Gujarat riots) die Gewalt gegen Muslime zu stoppen. Es gab wohl eine stillschweigende Übereinkunft mit Modi, dem damaligen Chefminister von Gujarat (ગુજરાત), der die Krawalle zugelassen hat. Advani hat auch die Gewalttaten gegen Christen in vielen Teilen Indiens als isolierte Unfälle bezeichnet oder sogar verteidigt - z.B. hat der Bajrang Dal (Hindi: बजरंग दल), eine Organisation des RSS, 1999 in Orissa (ଓଡ଼ିଶା) einen christlichen Vater mit seinen zwei Söhnen lebendig verbrannt. [vgl. Kuruvachira S. 104]
Seit 2014 kann man beobachten, wie die Ideologie des Sangh sich in Indien immer mehr durchsetzt [s. unten 5. Aktuelle Folgen der RSS-Ideologie]. Nur wenn es aus wahl-taktischen Gründen opportun erscheint, weicht die BJP von den Forderungen des RSS ab. So verurteilte Modi einen Teil der Kuhschützer als Störer, weil diese die Dalits gegen die Regierung aufgebracht haben. Das brachte Modi einen Vorwurf von Pravin Togadia (Hindi: प्रवीण तोगड़िया), dem Chef der VHP [Vishva Hindu Parishad -- Sanskrit/Hindi: विश्व हिंदू परिषद], und in Folge davon vom RSS ein, denn in früheren Zeiten hat Modi die Kuhschützer hoch gepriesen. Im Allgemeinen aber weist der RSS seine Mitgliedsorganisationen an, sich zurückzuhalten bei Kritik am Premierminister.
Ein Problem ist z.B. die Sprachenfrage in Goa (गोंय). Es geht dabei um 126 meist christliche English medium schools, die in den 1990er Jahren zu Konkani (कोंकणी) und Marathi (मराठी), den einheimischen Sprachen, übergegangen waren. Dann aber 2011 wieder zu Englisch gewechselt haben. In den Wahlen 2012 hatte die BJP versprochen diesen Schulen die Gelder zu sperren. Nach der Wahl wurde das von Seiten der BJP verzögert und führt zu Auseinandersetzung zwischen RSS und Partei. [Vgl.: Mahurkar, Uday: Crossed Lines : Goa (गोंय) revolt reveals rift in BJP-RSS ties. - In: India today. - Kindle ed. - 2016-09-19]
Es gibt auch Auseinandersetzungen wegen der Besetzung von Direktorenstellen in wichtigen öffentlichen Institutionen: die Modiregierung hat einige frühere Direktoren gegen den Willen der RSS nicht abgerufen bzw. einige nicht besetzt.

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Bharatiya Janata Yuva Morcha [BJYM] Hindi: भारतीय जनता युवा मोर्चा |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Jugendorganisation der BJP. |
| Präsident 2018 | Poonam Mahajan Rao Marathi: पूनम महाजन राव, 1980 - ) |
| Gegründet | 1978 |
| Hauptquartier | New Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | BJP |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.bjym.org
- Zugriff am 2018-02-17 (zusätzlich Webseiten im jeweiligen
Bundesland) https://www.facebook.com/search/top/?q=Bharatiya+Janata+Yuva+Morcha&init=public. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/bjym?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bharatiya_Janata_Yuva_Morcha. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
Die Struktur der Organisation entspricht der der Mutterpartei.
Unter Philosophie der Organisation wird Hindutva betont:
"Hindutva [Sanskrit: हिन्दुत्व] or Cultural Nationalism presents the BJP´s conception of Indian nationhood," [...] "It must be noted that Hindutva is a nationalist, and not a religious or theocratic, concept."
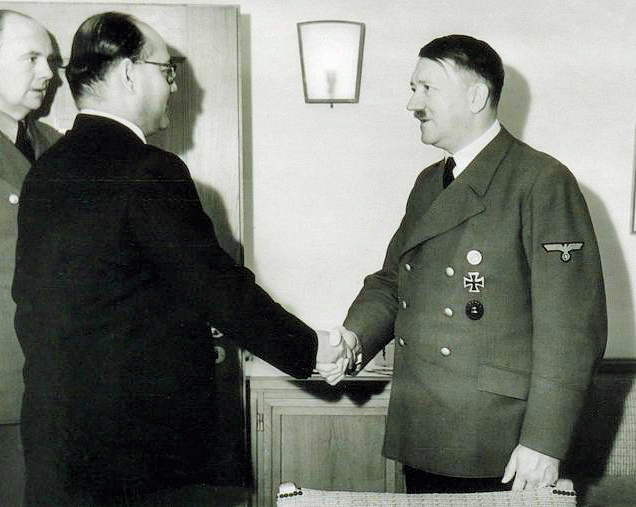

Abb.: Subhas Chandra Bose (Oriya/Bengali:
ସୁଭାଷ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ବୋଷ /
সুভাষ চন্দ্র
বসু) mit Adolf Hitler,
1941/42
[Public domain]
Als Vorbild wird Subhas Chandra Bose (Oriya/Bengali: ସୁଭାଷ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ବୋଷ / সুভাষ চন্দ্র বসু) genannt [s. http://www.bjymgujarat.org/hindutva.html - Zugriff am 2016-12-21]. Bose (1897 - 1945?, ob er 1945 bei einem Flugzeugabsturz ums Leben gekommen ist, ist noch umstritten) wollte die Unabhängigkeit Indiens mit militärischem Kampf erreichen. Er war Mitbegründer der Indischen Legion (der Waffen-SS unterstellt) und später der Indian National Army (der japanischen Armee unterstellt) [s. Subhash Chandra Bose. https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subhash_Chandra_Bose - Zugriff am 2016-12-21]
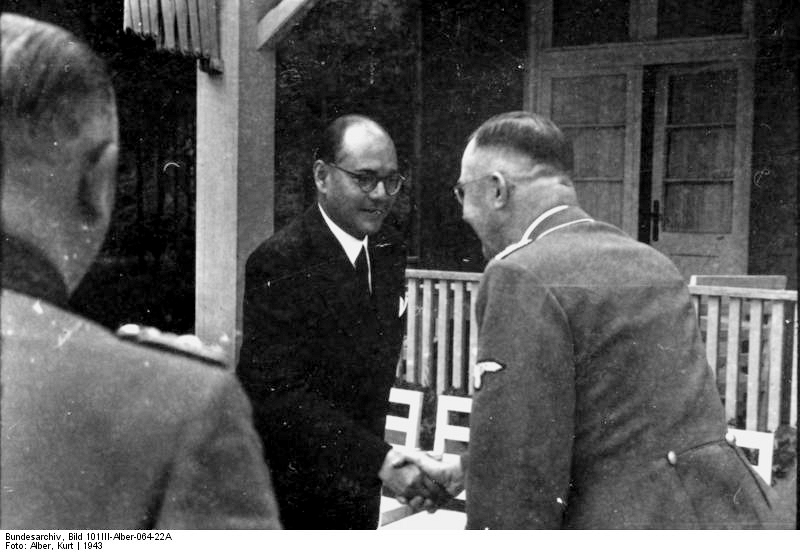

Abb.: Subhas Chandra Bose (Oriya/Bengali:
ସୁଭାଷ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ବୋଷ /
সুভাষ চন্দ্র
বসু) mit Heinrich
Himmler, Reichsführer SS, 1942
[Bildquelle: Bundesarchiv, Bild 101III-Alber-064-22A / Alber, Kurt /
CC-BY-SA 3.0]
Zur Zeit [2016] soll sich die Jugendorganisation im Programm "Youth for Digital Paisa" dafür einsetzen, dass Indien auf bargeldloses Bezahlen übergeht. Modi ruft die Jugend auf digitale Methoden für digitales Bezahlen zu verwenden. [s. Digital methods for Digital Payment. http://www.bjym.org/cat/bjym-news/ - Zugriff am 2016-12-21]
Das ist eins der Ziele hinter der "demonetisation" [es geht um Bargeld-Vernichtung]: am 8.11. 2016 erklärte Modi die 500 Rupiennote und die 1000 Rupiennote zu ungültigen Noten. Diese beiden Noten sind die, die in Indien am meisten verbreitet sind. Modi ist überzeugt, dass damit die Korruption eingedämmt wird und das Schwarzgeld ausgerottet wird. Außerdem soll das ein Schlag gegen die Naxalisten und Terroristen sein, weil ihr gesammeltes Geld ungültig wird. [Das Umtauschen der betroffenen Geldscheine war allerdings so schlecht vorbereitet, dass die Sache zu einer Katastrophe u.a. für die Armen Indiens (z.B. hatten die Bauern kein Geld mehr um Saatgut zu kaufen), für Händler und kleine Fabrik-Besitzer wird. Da nach Schätzungen nur etwa 6% von Indiens Schwarzgeld indisches Bargeld ist, steht der Verlust für die Wirtschaft in keinem Verhältnis zum gewonnenen Schwarzgeld. ][s. Dutt, Barkha: Is demonetisation a case of dynamism or disruption? In: Hindustan times. - Kindle ed. - 2016-12-17]
Die Jugendorganisation hat sich schon immer als Verteidiger der Nationalhymne und der Nationalflagge gesehen, nutzt jetzt aber das Urteil des Obersten Gerichtshofs vom November 2016 um die Leute, die im Kino während des Abspielens der Nationalhymne nicht aufstehen, der Polizei zu melden. [s. unten 5.2]

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Bharatiya Kisan Sangh - Hindi: भारतीय किसान संघ -- Indian Farmers' Association |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Indiens größte Bauernorganisation |
| Präsident 2018 | Prabhakar Kelkar (Hindi: प्रभाकर केलकर) |
| Mitglieder | 20 Millionen |
| Gegründet | 1979 |
| Hauptquartier | New Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | RSS |
| Webpräsenz | http://bharatiyakisansangh.org/
-- Zugriff am 2018-02-17 https://www.facebook.com/Bharatiya-Kisan-Sangh-320437964632942/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/KisanSangh?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bharatiya_Kisan_Sangh. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
2.1. Bharatiya Kisan Sangh [Hindi: भारतीय किसान संघ], literally, Indian Farmers' Association (8m)
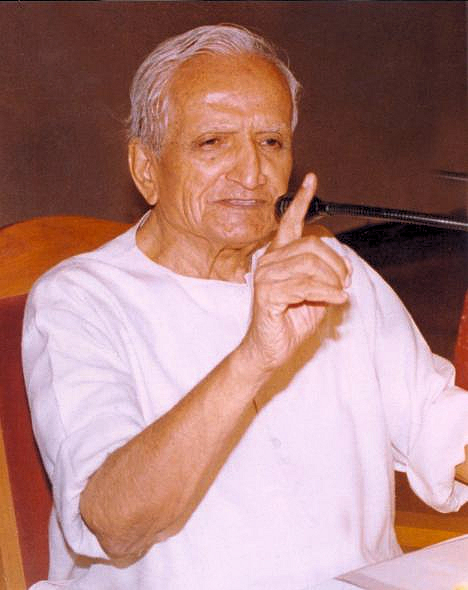

Abb.: Dattopant Bapurao
Thengadi, (Marathi: दत्तोपंत बापूराव ठेंगडी,
1920 – 2004)
[Public domain. --
CC0 1.0]
Die Organisation wurde 1979 von Dattopant Bapurao Thengadi, (Marathi: दत्तोपंत बापूराव ठेंगडी, 1920 – 2004), der auch an der Gründung von Bharatiya Mazdoor Sangh (Hindi: भारतीय मजदूर संघ -- Indian Labourers' Association) beteiligt war, gegründet. BKS kümmert sich um alle Belange der Bauern in Indien. Betont werden die Erfahrungen der Jahrhunderte alten Praktiken in der Landwirtschaft. Man wehrt sich z.B. gegen das Patentieren von landwirtschaftlichen Produkten. Seit 2011 verlangt man, dass Monsanto wegen Gen-veränderter Saaten Indien verlassen soll. BKS gibt u.a. an:
[Quelle: http://en.bharatiyakisansangh.org/static/history.aspx -- Zugriff am 2016-09-12]

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Bharatiya Mazdoor Sangh - Hindi: भारतीय मजदूर संघ -- Indian Labourers' Association |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Gewerkschaftsorganisation des Sangh |
| Präsident 2018 | Baij Nath Rai (Hindi: बैज नाथ राय) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | 11 Millionen (2010) |
| Gegründet | 1955 |
| Hauptquartier | New Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | Sangh Parivar - Hindi: संघ परिवार, RSS |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.bms.org.in/ -- Zugriff am
2018-02-17 https://www.facebook.com/Bhartiya-Mazdoor-Sangh-BMS-267369163284206/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/mazdoorsangh?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bharatiya_Mazdoor_Sangh. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
2.2. Bharatiya Mazdoor Sangh [Hindi: भारतीय मजदूर संघ], Indian Labourers' Association (10 million as of 2009)
Wurde 1955 von Dattopant Bapurao Thengadi, (Marathi: दत्तोपंत बापूराव ठेंगडी, 1920 – 2004, siehe oben) zusammen mit wenigen Personen gegründet. Ziel war es eine von der Politik unabhängige nationale Gewerkschaft zu bilden. 2002 war der BMS die größte Gewerkschaft in Indien. Laut Angaben der BMS hat sie inzwischen 10 Millionen Mitglieder mit über 5000 angeschlossenen Gewerkschaften in allen Industriezweigen.
BMS setzt sich ein
[http://bms.org.in/pages/BMSATGlance.aspx -- Zugriff am 2016-09-11].
So sieht BMS 2012-22-07 die indische Wirtschaft:
"Bharat has its own economics. It alone had the privilege of evolving a scientific socio-economic order based upon realisation of Universal Laws. Modern materialistic religions are too young to appreciate mature wisdom of this ancient land. Bharatiya Mazdoor Sangh aspires to represent this characteristically Bharatiya approach in the labour field of the country."
[Quelle: http://bms.org.in/encyc/2012/7/22/Economics-%E2%80%93-A-Bharatiya-View-Point.aspx -- Zugriff am 2016-09-11.
1.2.3. Bharatiya Railways Sangh [Hindi: भारतीय रेल्वे मजदूर संघ], Indian Railways Workers' Association

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Bharatiya Railways Sangh (BRMS) -- Hindi: भारतीय रेल्वे मजदूर संघ -- Indian Railways Workers' Association |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | Mangesh M Deshpande |
| Gegründet | 1962 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | http://brms.org.in/.
-- Zugriff am 2018-02-18
https://www.facebook.com/bharatiyarailwaymazdoorsangh/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/brmsunion?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Gewerkschaften des BRMS | 1. PURVOTTARA
RAILWAY SHRAMIK SANGH – PRSS 2. MADHYA RAILWAY KARMACHARI SANGH – MRKS 3. PASCHIMA RAILWAY KARMACHARI PARISHAD – PRKP 4. DAKSHINA PURVA RAILWAY MAZDOOR SANGH – DPRMS 5. UTTARA RAILWAY KARMACHARI UNION – URKU 6. PURVI RAILWAY KARMACHARI SANGH – PRKS 7. DAKSHINA RAILWAY KARMIK SANGH -DRKS 8. DAKSHINA MADHYA RAILWAY KARMIK SANGH -DMRKS 9. PURVOTTARA SEEMANT RAILWAY KARMACHARI SANGH -PSRKS 10. DAKSHINA PURVA MADHYA RAILWAY MAZDOOR SANGH-DPMRMS 11. UTTARA PURVA RAILWAY KARMACHARI SANGH- UPRKS 12. PURVA MADHYA RAILWAY MAZDOOR SANGH – PMRMS 13. EAST COAST RAILWAY MAZDOOR UNION -ECORMU 14. PASCHIMA MADHYA RAILWAY KARMACHARI SANGH -PMRKS 15. UTTARA MADHYA RAILWAY KARMACHARI SANGH -UMRKS 16. NAIRUTYA RAILWAY MAZDOOR SANGH -NRMS 17. CALCATTA METRO RAILWAY KARMACHARI SANGH – CMRKS 18. D.L.W MAZDOOR SANGH -DLWMS 19. D.C.W. KARMACHARI SANGH – DCWKS 20. CHITTARANJAN RAILENGINE KARKHANA KARMACHARI SANGH – CREKKS 21. I.C.F. KARMIK SANGH -ICFKS 22. R.C.F. KARMACHARI SANGH -RCFKS 23. RAIL WHEEL FACTORY EMPLOYEES SANGH -RWFES 24. BSCLKS -Burnpur 25. KONKAN RAILWAY MAZDOOR SANGH – KRMS 26. R.D.S.O MAZDOOR SANGH – RDSOMS |
| Wikipedia | --- |
1.2.4. Fishermen's Co-operative Societies (2.2m)
| Name | Fishermen's Co-operative Societies |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | 2 Millionen |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1913 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | |
| Wikipedia | --- |
1.2.5. Samskar Bharati [Hindi: संस्कार भारती], Organisation of Indian Artists

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Samskar Bharati -- Hindi: संस्कार भारती -- Organisation of Indian Artists |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1981 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.sanskarbharti.net/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-18 (In Hindi) |
| Wikipedia | --- |
1.2.6. Akhil Bharatiya Adhivakta Parishad, All India Lawyers' Council

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Akhil Bharatiya Adhivakta Parishad -- Hindi: अखिल भारतीय अधिवक्ता परिषद -- All India Lawyers' Council |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "resurrecting Bharatiya values and ingraining idealism in the hearts of advocates for improving efficacy and standards of the Bar and the Judiciary of the country." |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1992 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.adhivaktaparishad.com/.
-- Zugriff am 2019-02-18 https://www.facebook.com/AkhilBharatiyaAdhivaktaParishad/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/AdhivaktaP?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Akhil Bharatiya Vidyarthi Parishad (ABVP) - Hindi: अखिल भारतीय विद्यार्थी परिषदएबीवीपी -- All India Students' Council |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Studentenorganisation. |
| Präsident 2018 | S.Subbiah (Tamil: எஸ். சுப்பையா) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | 3 Millionen |
| Gegründet | 1949 |
| Hauptquartier | Mumbai (Marathi: मुंबई) |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.abvp.org/. -- Zugriff am
2018-02-18 https://www.facebook.com/ABVPVOICE/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/ABVPVoice?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Akhil_Bharatiya_Vidyarthi_Parishad. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
2.7. Akhil Bharatiya Vidyarthi Parishad [Hindi: अखिल भारतीय विद्यार्थी परिषद], All India Students' Council (2.8m)
Angaben von der Webseite: Mitglieder dieser Organisation sehen sich als ein führender Teil einer patriotischen nationalistischen Bewegung und eines sich ändernden Indiens ("prominent part of a Patriotic Nationalist movement and a changing Bharat.")
Laut ABVP handelt es sich um die größte Studentenorganisation der Welt.
Die wichtigsten Aktivitäten sind:
1.2.8. Akhil Bharatiya Shaikshik Mahasangh [अखिल भारतीय शैक्षिक महासंघ], All India Teachers' Federation (1.8m)

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Akhil Bharatiya Shaikshik Mahasangh -- Hindi: अखिल भारतीय शैक्षिक महासंघ -- All India Teachers' Federation |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "Akhil Bhartiya Rashtriya Shaikshik Mahasangh (ABRSM) is an organisation imbued with Indianness with an aim to propagate the ideology of Cultural Nationalism in the field of education and society. Along with safeguarding teachers' interests including their salary, allowances, service conditions and other facilities, the Mahasangh keeps in mind its national objectives, plans and executes the programmes of social concern and educational upgradation. " (https://www.abrsm.in/about-us.htm. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-18) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | Vimal Prasad Agrawal |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | https://www.abrsm.in/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-18 |
| Wikipedia | --- |

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | National Medicos Organisation [NMO] |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Organisation von qualifizierten Ärzten und Studierenden der Medizin in Indien |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1977 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.nmomh.com
- Zugriff am 2018-02-18 https://www.facebook.com/bharatnmo/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/MedicosOrg?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
2.9. National Medicos Organisation, Organisation of Medical Practitioners
Die Organisation beschreibt sich als führende Organisation von qualifizierten Ärzten und Studierenden der Medizin in Indien. Das Ziel ist
"to organize and motivate allopathic doctors for serving under-privileged sections of the society, settled in the tribal village and slum areas of Bharat."
[Homepage der NMO] [Allopathie ist eine Heilmethode der Schulmedizin.]
Die Organisation fördert neben der Motivation zum freiwilligen Dienst im Gesundheitsbereich Patriotismus, indische Kultur und Sanskar [Hindi: संस्कार]
[Definition von Sanskar für Kinder:
is multiplication of virtues and division of personality defects.‘Multiplication of virtues’ means enhancing virtues in self and ‘division of personality defects’ means reduction of personality defects in self. Sanskar also means ‘making good or purifying.’ In this process we are supposed to remove our shortcomings.
https://www.hindujagruti.org/hinduism-for-kids/433.html - Zugriff am 2017-09-28]
Die Organisation hat etwa 2000 Ärzte als lebenslange Mitglieder und etwa 5000 Ärzte, die der Organisation verbunden sind. Im September 2017 fühlten sich diese in ihren religiösen Gefühlen wegen einer Anzeige eines Kondom-Herstellers belästigt: auf Werbetafeln mit einem Foto von Sunny Leone [Panjabi: ਸਨੀ ਲਿਓਨ, 1981 - ] war zu lesen:

आ नवरत्रिओ रमो, परंतु प्रेमथी
"This Navratri, play, but with love".
Abb.: Plakat für MANforce. -- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7l31ft-brzc. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-06 -- Fair use
Also hat die Organisation mit Unterstützung des RSS und von Vishwa Hindu Parishad aufgefordert, dass nicht nur die Kondome sondern alle Medikamente von Mankind Pharma [Webpräsenz: https://www.mankindpharma.com/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-06] boykotiert werden sollen, weil die Kultur der Hindus beleidigt und die Hindus aufhetzt.
"doctor Vasant Patel told Mirror: "The message in the hoarding was very clear that condoms should be used during Navratri. I think legal action must be initiated against this company."
[s. Gujarat (ગુજરાત) Doctors Affiliated To The RSS Boycott Condom Brand Endorsed By Sunny Leone For This Confusing 'Reason' Some sanskaar a day, keeps condoms away. - 21.9.21017 - http://www.huffingtonpost.in/2017/09/21/Gujarat (ગુજરાત)-doctors-affiliated-to-the-rss-boycotting-condom-brand-endorsed-by-sunny-leone-for-this-confusing-reason_a_23217306/?utm_hp_ref=in-homepage - Zugriff am 2017-09-28]
1.2.10. Akhil Bharatiya Poorva Sainik Seva Parishad [Hindi: अखिल भारतीय पूर्व सैनिक सेवा परिषद], (ABPSSP) All India Ex-Military Servicemen Council.

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Akhil Bharatiya Poorva Sainik Seva Parishad (ABPSSP) -- Hindi: अखिल भारतीय पूर्व सैनिक सेवा परिषद -- All India Ex-Military Servicemen Council. |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | V. M. Patil |
| Gegründet | 1995 |
| Hauptquartier | New Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.abpssp.org/.
- Zugriff am 2018-02-18
https://www.facebook.com/abpssppta. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/abpsspdelhi?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Swadeshi Jagaran Manch [oder: Swadeshi Jagran Manch, SJM] - Hindi: स्वदेशी जागरण मंच -- Nativist Awakening Front |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Wirtschaftsflügel des RSS, die Organisation für ökonomische Unabhängigkeit. |
| Präsident 2018 | Ashwani Mahajan (Hindi: अश्वनी महाजन) |
| Gegründet | 1991 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | RSS |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.swadeshionline.in/
-- Zugriff am 2018-02-19 https://www.facebook.com/swadeshijagranmanch/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swadeshi_Jagaran_Manch. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
3.1. Swadeshi Jagaran Manch [स्वदेशी जागरण मंच], Nativist Awakening Front
SJM wurde 1991 gegründet, um das Konzept der wirtschaftlichen Unabhängigkeit zu verteidigen. Das Swadeshi-Konzept (Sanskrit: स्वदेशी) wurde schon im Unabhängigkeitskampf Indiens als sehr wichtig angesehen. Führende Freiheitskämpfer wie Lokmanya Tilak (Marathi: बाळ गंगाधर "लोकमान्य" टिळक, 1856 - 1920), Veer Savarkar (Marathi: विनायक दामोदर "वीर" सावरकर, 1883 - 1966), Shri Aurobindo (Bengali: অরবিন্দ ঘোষ, 1872 - 1950) und Mahatma Gandhi (Gujarati: મોહનદાસ કરમચંદ ગાંધી, 1869 - 1948) vertraten das Konzept, dass völlige wirtschaftliche Freiheit für das Leben notwendig ist. Schon 1980 gab es Kampagnen gegen wirtschaftlichen Imperialismus u.a. von den Organisationen Bharatiya Mazdoor Sangh (Hindi: भारतीय मजदूर संघ), Bharatiya Kisan Sangh (Hindi: भारतीय किसान संघ) und Akhil Bharatiya Vidyarthi Parishad (Hindi: अखिल भारतीय विद्यार्थी परिषदएबीवीपी).
Heute hat SJM ein Netzwerk über ganz Indien gebildet und arbeitet mit vielen Organisationen zusammen um die indische Wirtschaft unabhängig vom Ausland zu machen.
"Promotion of Swadeshi products, arranging help in development of professionals, cultural & value oriented Indian Corporate Structure, [...] intellectual support center and awards to master craftsmen & producers for excellent Swadeshi Products are some of the dimensions in which SJM has worked with marked success. In short, Swadeshi Jagran Manch has emerged as a forceful mobilization, with a vision and action plan for a truly self reliant Bharat and equitable world order, that nobody can afford to ignore."
[Quelle: http://www.swadeshionline.in/content/introduction -- Zugriff am 2016-09-09].
Man kämpft gegen Multinationale wie Pepsi, Monsanto, gegen WTO (World Trade Organization) und gegen jedes Investment aus dem Ausland, was inzwischen zu Auseinandersetzungen mit der Modi-Regierung führt, denn Modis Wirtschaftskonzept geht von Investitionen aus dem Ausland aus, um die kränkelnde Wirtschaft Indiens zu retten.
1.3.2. Bhartiya Vitta Salahkar Samiti, Financial consultants' association

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Bhartiya Vitta Salahkar Samiti (BVSS) -- Financial consultants' association |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "Nation Building through Cultural Nationalism, Integral Humanism, Enriched Professionalism. " |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | 900 (2012) |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1999 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | https://www.facebook.com/bvssonline/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-18 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
1.3.3. Laghu Udyog Bharati -- Hindi: लघु उद्योग भारती, an extensive network of small industries.

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Laghu Udyog Bharati -- Hindi: लघु उद्योग भारती |
|---|---|
| Funktion | All India organization of Micro and Small Industries in India |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1994 |
| Hauptquartier | New Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | http://lubindia.com/.
-- Zugriff am 2018-02-18
https://www.facebook.com/lubindia/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/lubindia?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
1.3.4. Sahakar Bharati -- Hindi: सहकार भारती Organisation of co-operatives

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Sahakar Bharati -- Hindi: सहकार भारती |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "the Sahakar Bharati envisages and endeavors to create a strong and devoted cadre of selfless and dedicated Co-Operators who would be well equipped for spreading the knowledge of the Co-Operative Movement which in the present circumstances can only act as the ‘savior’ for upliftment of Vanavasis (Tribals), Small farmers, Landless Labourers, Rural Artisans, Jobless Technicians and Consumers from the middle and lower income groups." (https://sahakarbharti.org/index.php/about-us/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-18) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1978 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | https://sahakarbharti.org/.
-- Zugriff am 2018-02-18 https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100005467487372. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Deendayal Reseach Institute - Deendayal Shodh Sansthan -- Hindi: दीनदयाल शोध संस्थान |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "to validate the philosophy of "Integral Humanism". Models for development such as providing services for health, hygiene, basic education, training for self employment etc. have been developed to achieve overall socio-economic development and reconstruction of Indian Society. The developmental programmes" ( http://chitrakoot.org/driindia/home.html. -- Zugriff am 2018-03-18. -- Fair use) |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1968-03-08 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | siehe die Übersicht aller
Institutionen:
http://deendayalupadhyay.org/sevakarya.html. -- Zugriff am
2018-02-18 http://chitrakoot.org/driindia/home.html. -- Zugriff am 2018-03-18 https://www.facebook.com/Pt-Deen-Dayal-Upadhyaya-Institute-for-the-Physically-Handicapped-120233921332972/?hc_ref=ARRk-hfCdZXs0Ey9BIlwZrqknFvy2LnpIEsWKzw3RU6sW3qktanXfHQ6unM5-LdVuII. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
4.1. Deen Dayal Shodh Sansthan, for the development of rural areas on the basis of Integral Humanism (1.7m)
Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay (Hindi: दीनदयाल उपाध्याय, 1916 – 1968) was an eminent Indian thinker, social worker and politician who was one of the leaders of the Bharatiya Jana Sangh, the forerunner of the present day Bharatiya Janata Party.
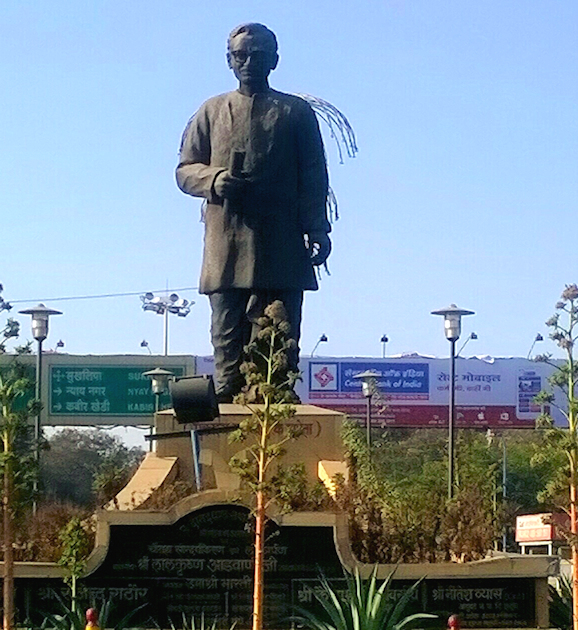

Abb.: Deendayal Upadhyay (Hindi: दीनदयाल उपाध्याय,
1916 – 1968) Statue in Indore (Hindi: इंदौर), 2016
[Bildquelle: Vedansh Sharma/Vivek Tiwari/Wikimedia. --
CC BY-SA 4.0]
1.4.2. Bharat Vikas Parishad, Organization for the development & growth of India in all fields of human endeavor (1.8m)

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Bharat Vikas Parishad -- Hindi: भारत विकास परिषद |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "Bharat Vikas Parishad is a service-cum-sanskar oriented, non-political, socio-cultural voluntary organisation. It is dedicated to the development and growth of our country in all fields of human endeavour - cultural, social, academic, moral, national and spiritual - by promoting a sense of patriotism, national unity and integrity. " (http://www.bvpindia.com/parishad_sutra.html. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-19) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | Sitaram Pareek |
| Gegründet | 1963 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.bvpindia.com/.
-- Zugriff am 2018-02-19
https://www.facebook.com/bharat.vikasparishad.5. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
"1963 12th January: Citizens Council, set up by Dr. Suraj Parkash initially to mobilize citizens’ efforts to fight the Chinese attack, was renamed as the Bharat Vikas Parishad (BVP) on the birth centenary of Swami Vivekanand (Bengali: বিবেকানন্দ, 1863 - 1902) and thus BVP was born. Shri B. P. Sinha, Retd. Chief Justice of Supreme Court becomes the first Chief Patron, Lala Hans Raj Gupta, the first President and Dr. Suraj Parkash its first Secretary General." (http://www.bvpindia.com/history.html. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-19)
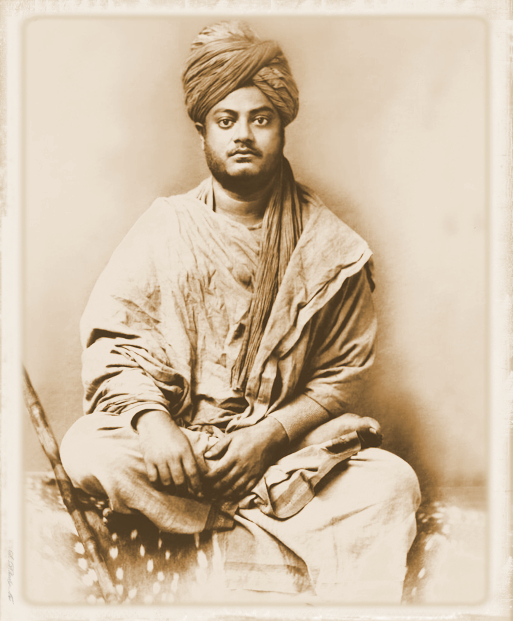

Abb.: Swami Vivekananda (Bengali:
বিবেকানন্দ,
1863 - 1902)
[Public domain]
4.3. Swami Vivekananda Medical Mission, Sociomedical Services (1.7m)

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Swami Vivekananda Medical Mission |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "Swami Vivekananda Medical Mission is a registered Charitable trust working with a not for profit motive. The trust aims to serve the backward sections of the population of Attappady [Malayalam: അട്ടപ്പാടി] block of Palakkad [Malayalam: മണ്ണാർക്കാട്] district in Kerala [Malayalam: കേരളം] state, India." (http://www.missionvivekananda.org/ . -- Zugriff am 2018-02-19) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | V.P.S. Menon |
| Gegründet | 2002 |
| Hauptquartier | Attappady -- Malayalam: അട്ടപ്പാടി |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://www.missionvivekananda.org/
. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-19 https://www.facebook.com/missionvivekananda/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/svmmagali. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
4.4. Sewa Bharati [Hindi: सेवा भारती], Organisation for service of the needy (founded in 1984)

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Sewa Bharati -- Hindi: सेवा भारती |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Community service: Sewa Sanskar Samrasta Samridhi -- Hindi: सेवा संस्कार समृद्धि समरसता (Dienst, Befähigung, Harmonie, Wohlstand) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | Tarun Gupta |
| Gegründet | 1979 |
| Hauptquartier | New Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | https://www.sewabhartidelhi.org/.
-- Zugriff am 2018-02-19
https://twitter.com/sewabharati?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Seva_Bharati. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
4.5. Sakshama, an organization working among the blind

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Sakshama -- Kannada: ಸಕ್ಷಮ |
|---|---|
| Funktion | development & welfare of persons with disabilities |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | Bengaluru -- Kannada: ಬೆಂಗಳೂರು |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | http://sakshamakarnataka.org/.
-- Zugriff am 2018-02-19 https://www.facebook.com/sakshama.karnataka. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/SakshamaKA?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
4.6. Hindu Seva Pratishthana -- Kannada: ಹಿಂದು ಸೇವಾ ಪ್ರತಿಷ್ಠಾನ

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Hindu Seva Pratishthana -- Kannada: ಹಿಂದು ಸೇವಾ ಪ್ರತಿಷ್ಠಾನ |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "HSP is committed to the upliftment of the under – served and people with special needs without discrimination on the basis of caste, creed or religion. Through service HSP aims to bring about a transformation in the society where people and communities are self-reliant. The instruments of this change are Sevavratis – young men and women volunteers – many of them who dedicate their lives fully to the noble cause of serving the society." ( http://hinduseva.org/about-us/vision-and-mission/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-19) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 |
Shri Shri Vishwesha Teertha Swamiji Pejawar Math , Udupi |
| Gegründet | 1980 |
| Hauptquartier | Bengaluru -- Kannada: ಬೆಂಗಳೂರು |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://hinduseva.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-19
https://www.facebook.com/HSPKarnataka/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/HSPKarnataka. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
HSP has 9 core focus areas of work.
4.6.1. Nele

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Nele |
|---|---|
| Funktion | residential care to destitute children |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 2000 |
| Hauptquartier | Bengaluru -- Kannada: ಬೆಂಗಳೂರು |
| Mutterorganisation | Hindu Seva Pratishthana -- Kannada: ಹಿಂದು ಸೇವಾ ಪ್ರತಿಷ್ಠಾನ |
| Webpräsenz | http://nelehsp.org/.
-- Zugriff am 2018-02-19
https://www.facebook.com/NeleHSP/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/NeleHSP. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
"So far, 10 centres have been established 6 in Bangalore [Kannada: ಬೆಂಗಳೂರು] and others in Mysore [Kannada: ಮೈಸೂರು], Tumkur [Kannada: ತುಮಕೂರು], Shimoga [Kannada: ಶಿವಮೊಗ್ಗ] and Bagalkote [Kannada: ಬಾಗಲಕೋಟೆ ]. Over 260 boys and girls have found caring homes in these centers." (http://nelehsp.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-19)

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Rashtra Sevika Samiti - Hindi: राष्ट्र सेविका समिति -- National Volunteer Association for Women |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Frauenorganisation des RSS. |
| Präsident | V. Shantha Kumari -- Hindi: वी. शान्ताकुमारी (1952 - ) |
| Gegründet | 1936 |
| Hauptquartier | Nagpur -- Hindi: नागपुर |
| Mutterorganisation | RSS |
| Webpräsenz | http://rashtrasevikasamiti.org - Zugriff am 2018-02-19 (nur in Hindi)
https://www.facebook.com/Rashtra-Sevika-Samiti-189079117892184/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rashtra_Sevika_Samiti. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
Rashtra Sevika Samiti [Hindi: राष्ट्र सेविका समिति], literally, National Volunteer Association for Women (1.8m)
Es handelt sich um die Parallelorganisation zum RSS für Frauen, gegründet von Laxmibai Kelkar (Hindi: लक्ष्मीबाई केलकर, 1905 - 1978) 1936 nach Absprache mit K. B. Hedgewar (Hindi: केशव बलिराम हेडगेवार, 1889 - 1940), dem Gründer des RSS, weil die Mitgliedschaft im RSS sich nur auf Männer bezieht. Es ist die größte Organisation für Hindufrauen, die auch Zweigorganisationen in weiteren Ländern hat (unter der Bezeichnung "Hindu Sevica Samiti"). Die Frauen sind aktiv in sog. Shakhas (Sanskrit/Hindi: शाखा), das sind lokale Gruppen, die sich regelmäßig treffen um Yoga zu praktizieren, nationalistische Lieder zu singen und auch militärisches Training durchzuführen. Z.B. wurden aus Anlass des 150. Geburtstags von Vivekananda (Bengali: বিবেকানন্দ, 1863 - 1902) 500 Lager organisiert, in denen Kampfsportarten trainiert wurden. [Quelle: http://hssuk.org/samiti/ -- Zugriff am 2016-08-19]. Über ganz Indien verteilt gibt es etwa 55 000 Shakhas [Stand von 2013 s. Dixit, Neha: Holier than cow. - In: Outlook http://www.outlookindia.com/magazine/story/holier-than-cow/283593 -- Zugriff am 2016-08-19].
Die Organisation verteidigt ein traditionelles Frauenbild: Betonung der Mutterschaft, Unterordnung unter den Mann, Dienst an der Familie.
Dazu kommt die Verpflichtung, sich für "Hindu Rashtra" [Hindi: हिंदू राष्ट्र] d.h. eine Hindu-Nation einzusetzen.
Man versucht insbesondere junge Mädchen (z.B. durch Ferienlager für Mädchen von 5 bis 8 Jahren) und weibliche Jugendliche zu indoktrinieren. Die Pracharikas (Sanskrit/Hindi: प्रचारिका) - meist hauptamtliche ledige Mitarbeiter der Organisation, - bekommen eine Ausbildung in der Hindutva-Theorie und Kampfsportarten, sie sind beauftragt, möglichst viele neue Shakhas zu gründen. Dazu besuchen sie z.B. Stammesgebiete, in denen die Menschen Anhänger von Stammesreligionen, christlichen Kirchen oder dem Islam sind. Ziel ist es alle Inder wieder zum Hinduismus zu bekehren, denn man geht davon aus, dass alle Einwohner Indiens früher Hindus waren. Die Wirkung dieser Frauenorganisation darf nicht unterschätzt werden, denn in Indien kümmern sich vor allem die Frauen darum, dass die religiösen Rituale durchgeführt werden, also z.B. die täglichen Pujas (Sanskrit: पूजा) zu Hause und die Teilnahme an Pujas in Tempeln, das Einhalten der unterschiedlichen Fastengebote, das Unternehmen von Pilgerreisen, und je nach Kastenangehörigkeit das Befolgen der Gebote zu Reinheit und Unreinheit. Auch das Vorziehen der Söhne zu Ungunsten der Töchter ist bei indischen Müttern durchaus noch zu beobachten.
1.5.2. Shiksha Bharati [Hindi: शिक्षा भारती] (2.1m), to provide education and training for skill up gradation to underprivileged girls and women.

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Shiksha Bharati -- Hindi: शिक्षा भारती |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "To provide education and training for skill up gradation and lifelong learning to girls and women belonging to underprivileged sections of the society." (https://www.shikshabharati.com/about-us/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-19) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | Swati Garg -- Hindi: स्वाती गर्ग |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | Hapur -- Hindi: हापुड़ |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | https://www.shikshabharati.com/.
-- Zugriff am 2018-02-19
https://twitter.com/shiksha_bharati. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Durga Vahini - Hindi: दुर्गा वाहिनी [Armee der Durga] |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Organisation der Vishva Hindu Parishad für weibliche Jugendliche zwischen 15 und 35 Jahren |
| Präsident 2018 | Sadhvi Ritambhara -- Hindi: साध्वी ऋतम्भरा |
| Gegründet | 1984 |
| Hauptquartier | New Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | Vishva Hindu Parishad |
| Webpräsenz | bei Vishva Hindu Parishad: http://vhp.org/vhp-glance/youth/durga-vahini/ - Zugriff 2018-02-19. |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Durga_Vahini. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
5.3. Durga Vahini [Hindi: दुर्गा वाहिनी], Women's wing of Vishwa Hindu Parishad.
gegründet 1984-85 unter der Verantwortung von Sadhvi Rithambara (Hindi: साध्वी ऋतम्भरा [s. unten 3. ihre Rede in Hyderabad, 1991] .
Die Aufgaben entsprechen denjenigen von Bajrang Dal, gelobt wird das Mitmachen bei den Auseinandersetzungen um den Ram-Tempel in Ayodhya (अयोध्या), betont wird der Kampf gegen die Missionierung für fremden Glauben, die Bereitschaft zur Unterstützung von Witwen, verlassenen Frauen und allgemein hilfsbedürftigen Frauen, die Ausbildung zur Selbstverteidigung und zur Verteidigung der Hindu-Gesellschaft und die Pflicht zur Teilnahme an Gebetstreffen und kulturellen Tätigkeiten. Man legt Wert auf die Rekrutierung von Frauen aus armen Familien und unteren Kasten, diese lernen dann Karate und mit Stöcken zu kämpfen.
Unter den wichtigen Punkten z.B:
"05. Ideal of Durga Vahini would be Durga (Sanskrit: दुर्गा) and its motto Service, Security and Sanskar (Sanskrit: संस्कार)" [a.a.O.]
[Gemäß den Puranas ist Durga die Göttin, die den gefährlichen Büffeldämon Mahishasura (Sanskrit: महिषासुर) zusammen mit seinem Heer erschlägt.] [Sanskar = Leben gemäß der Werte des Hinduismus]
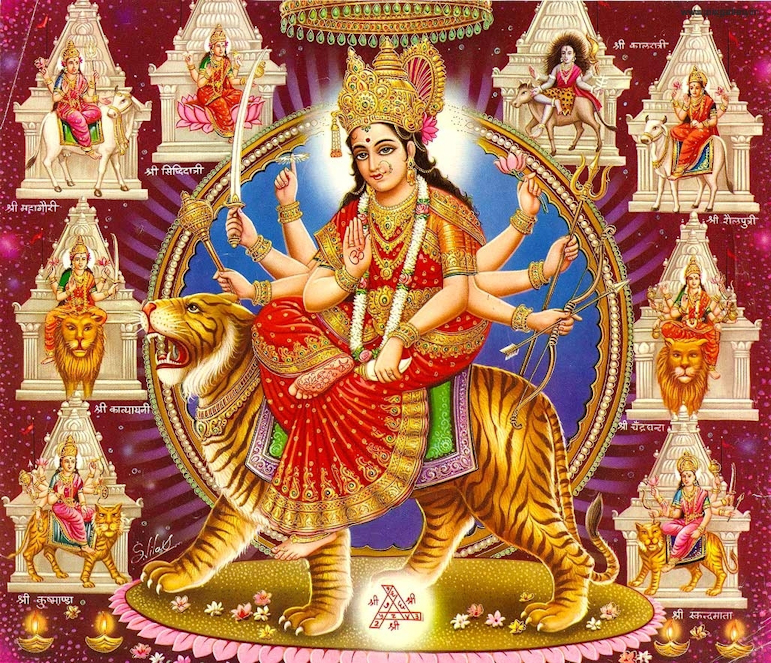

Abb.: Durga (Sanskrit:
दुर्गा)
[Bildquelle: Dinurmilayadav/Wikimedia. --
CC BY-SA 4.0]

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Vishwa Hindu Parishad (VHP) [Weltrat der Hindus] - Sanskrit/Hindi: विश्व हिंदू परिषद -- World Hindu Council |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Propagandaorgan des Sangh Parivar. |
| Präsident 2018 | Raghava Reddy -- Telugu: రాఘవ రెడ్డి |
| Gegründet | 1964 |
| Hauptquartier | New Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | Sangh Parivar - Hindi: संघ परिवार |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.vhp.org.
-- Zugriff am 20118-02-19
https://www.facebook.com/VhpVishwaHinduParishadAllIndia/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vishva_Hindu_Parishad / https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vishva_Hindu_Parishad. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22. |
1.6.1. Vishwa Hindu Parishad [Hindi: विश्व हिंदू परिषद], World Hindu Council (2.8m)
VHP wurde 1964 gegründet, weil man befürchtete, dass die Zahl der Hindus weltweit durch Konversion zum Christentum, zum Islam oder zum Kommunismus abnehmen könnte:
"The objective of the VHP is to organise - consolidate the Hindu society and to serve - protect the Hindu Dharma [Sanskrit: हिन्दूधर्म]. A strong effective, enduring and an ever increasing presence of VHP is seen in lakhs of villages & towns in Bharat [Sanskrit: भारत]. With an increased Hindu activity all over the world, a strong & self confident Hindu organisation is slowly taking shape."
[Quelle: Vishva Hindu Parishad. - 2010. - http://vhp.org/swagatam/ - Zugriff am 2016-08-27].
Die VHP arbeitet mit über 32 000 Projekten auf der Graswurzelebene der Hindu-Gesellschaft: im Gesundheitsbereich, in der Bildung, gegen die Unberührbarkeit.
VHP setzt sich ein für die wichtigsten Werte, den Glauben und die Traditionen der Hindus, insbesondere:
In den Worten des ersten General-Sekretärs Shivram Shankar Apte (Marathi: शिवराम शंकर आपटे, 1907 - 1985), einem Pracharak (प्रचारक) des RSS:
"The only way for the Hindu Society to save itself from the foreign onslaught of Christianity, Islam and communism is to organise itself."
Unter dem Begriff Hindu sind alle Menschen zu verstehen,
"who believe in, respect, of follow, the eternal values of life that have sprung up in Bharat [Sanskrit: भारत]."
Die Gesetze der Hindus beruhen auf:
"The Code of Manu, which as the supreme law of personal and social life, has governed and regulated the Hindu world for over last two thousand years, prescribes an ideal behavior for `Man´, and recommends it as worthy to be copied by the whole humanity".
[s. Apte, S.S.: Why Vishva Hindu Parishad. - [1964?]. - http://vhp.org/organization/org-why-vishva-hindu-parishad/. - Zugriff am 2018-02-19].
Buddhisten, Jainas und Sikhs (Panjabi: ਸਿੱਖੀ) werden zu den Hindus gerechnet. [s. auch die Jugendorganisationen Bajrang Dal und Durga Vahini]

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Bajrang Dal - Hindi: बजरंग दल |
|---|---|
| Funktion | eine militante Organisation der Vishwa Hindu Parishad für junge Männer |
| Präsident 2018 | Rajesh Pandey -- Hindi: राजेश पाण्डे |
| Gegründet | 1984 |
| Hauptquartier | New Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | Vishwa Hindu Parishad |
| Webpräsenz | auf der Seite von Vishwa Hindu Parishad:
http://vhp.org/vhp-glance/youth/dim1-bajrang-dal/
. - Zugriff am 2018-02-21 https://www.facebook.com/BajrangDal.Official/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/bajrangdalorg?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2028-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bajrang_Dal. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21. |
6.2. Bajrang Dal [Hindi: बजरंग दल], Army of Hanuman (2m)
1984 hatte Vishwa Hindu Parishad sich entschlossen eine Ram-Janaki Rath Yatra (Hindi: राम जानकी यात्रा) durchzuführen: eine Pilgerreise zur Erweckung der Hindu-Gesellschaft,
"but certain anti-Hindu and anti-social elements threatened with dire consequences if Vishwa Hindu Parishad organized this Yatra." [a.a.O.]
Da die Regierung von Uttar Pradesh (उत्तर प्रदेश) sich weigerte die Pilgerreise zu schützen, wurden junge Männer aufgerufen, den Schutz zu übernehmen und nach Ayodhya (अयोध्या) zu kommen. Daraus entwickelte sich Bajrang Dal. Die Organisation ist beteiligt an der Ram Janma Bhumi (Sanskrit/Hindi: राम जन्मभूमि) Bewegung (Tempel für Ram in Ayodhya (अयोध्या)) und war wesentlich beteiligt an der Zerstörung der Babri-Moschee (بابری مسجد) ( 1992 ) und der Verfolgung von Muslimen in den Gujarat(ગુજરાત)-Aufständen. Die Mitglieder der Organisation werden Karsevaks (Hindi: कारसेवक) genannt [das sind Freiwillige, die einen Dienst für eine religiöse Sache leisten, meistens bezogen auf den Bau einer religiösen Stätte] .
"Such a youth power was associated with it that was absolutely not ready to tolerate any symbols of insult to the Hindu society and which was prepared for any type of sacrifice for the protection of country and Dharma". [a.a.O.]
Abgesehen vom Kampf um den Tempel in Ayodhya (अयोध्या) nennt Bajrang Dal folgende Aufgaben :
Bajrang Dal organisiert regelmäßig Lager für seine Mitglieder, in denen sie mit Dreizacks [Trishul (Sanskrit/Hindi: त्रिशूल), eine Stichwaffe, ein Symbol Shivas] und in denen sie mit Gewehren, Schwertern und Stöcken üben, da die Organisation davon ausgeht, dass Polizei und Politiker zu wenig tun um die Hindu-Gesellschaft zu schützen.
Dazu Ravi Anant, ein VHP-Führer:
"In Bajrang Dal, these all are done to build character and generate nationalistic feeling among youth. There are different programmes, some are for the physical well-beeing whereas others are for mental well-being."
[Quelle: FIR against Bajrang Dal activists for organising arms training camp. - 2016-05-25. - In: http://zeenews.india.com/news/uttar-pradesh/fir-against-bajrang-dal-activists-for-organising-arms-training-camp_1888711.html - Zugriff am 2016-08-28]
Von diesem Lager im Mai 2016 in Ayodhya (अयोध्या) wurde
ein Video im Internet veröffentlicht, in dem man sehen konnte wie Bajrang
Dal-Kader übten Männer zu töten, die als Muslime verkleidet waren. [vgl.:
VHP president Praveen Togadia visits Bajrang Dal´s 'self-defence' camp in Noida
[
"The affable manner of forty-year-old Sharan Pampwell, the Mangalore-based [Kannada: ಮಂಗಳೂರು] leader of the Bajrang Dal in Karnataka [Kannada ಕರ್ನಾಟಕ], belies his exceptional business acumen. Like a good entrepreneur - obeying the laws of demand and supply - he has put to good use the anxiety felt by local businessmen as a direct result of the Bajrang Dal’s activities. He offers them protection by using the foot soldiers of the very same Hindutva outfit he represents. The enterprise he has reared thus works both ways: the businessmen get security from the Bajrang Dal, and the Bajrang Dal activists benefit from regular employment in the establishments rendered vulnerable by their own acts of violence and hooliganism. ‘We strictly follow the rules of business,’ Sharan tells me as I sit down with him to understand the economics of his politics. ‘Businessmen are prepared to work with us because we offer them security services at a very reasonable rate.’ Politics may once have been the sole reason for the existence of the Bajrang Dal - an aggressive youth brigade of the VHP, in turn an offshoot of the RSS - but in Mangalore, where this organization is very active today, it is a convincing profit motive that seems to drive its activities.
It works like this: first, the demand is created through the Bajrang Dal’s agitational activities, which range from vigilantism to hooliganism to vandalism. This creates a sense of insecurity among owners of malls, shops and apartments. Then Eshwari Manpower Solutions Limited, a company owned by Sharan, offers security guards to the terrified businessmen so their fears are assuaged. The manpower for both these activities is drawn from the same pool. ‘All the supervisors and the majority of the security guards who work for the company are Bajrang Dal karyakartas,’ says Sharan. ‘As the leader of the Bajrang Dal in this city, it is my duty to secure a livelihood for the karyakartas. But I don’t turn away anyone who comes to me for a job. There is enough demand for security guards in the city. Some of our guards are even Muslims.’
Sharan Pampwell has had a meteoric rise in the Bajrang Dal since joining the organization in 2005. In 2011 he became the convener of the Mangalore division, and in 2014 was given the same designation in the south Karnataka region. In the Bajrang Dal’s organizational structure, the state of Karnataka is divided into two units, north and south, each with its own convener. While in northern Karnataka the Bajrang Dal is weak, in the south it is hyperactive, perhaps far more than in any other part of the country.
[...]
The transformation of the Bajrang Dal into a protection racket is not necessarily the natural progression of street-level Hindutva politics. It has been possible in Mangalore because of the widespread perception among businessmen and ordinary citizens that appealing to the police for protection is futile. When the state is unable to rein in troublemakers and the government’s law and order machinery appears overwhelmed by them, perhaps the only option is to cooperate with the perpetrators of criminal culture."
[Quelle: Jha, Dhirendra K.: Shadow armies : fringe organizations and foot soldiers of Hindutva. -- New Delhi : Juggernaut, 2017. --229 S. -- ISBN 978-93-8622-824-6. -- S. 61f., 64 . -- Fair use]
"As it stands today, most Bajrang Dal activists are poorly educated young people who are either unemployed or who regard their jobs as unsatisfactory. Though the leadership belongs to the upper or intermediary castes, a substantial segment of the foot soldiers is drawn from the backward castes and even dalits. They are generally not interested in the doctrinal rigour or discipline that exists in the RSS shakhas and are keen to assert themselves by fighting those the Sangh Parivar prefers to treat as the other’ - mainly Muslims and Christians. This does not, however, mean that simply acquiring a new identity makes lower-caste Bajrang Dal members always forget the socio-economic frustrations that drove them into the Hindutva fold. Caste-based discrimination makes the frustration erupt rather unusually sometimes. This can be seen, for instance, in the splitting of the Bajrang Dal’s Mangalore unit which paved the way for the formation of the Sri Ram Sene." [Quelle: Jha, Dhirendra K.: Shadow armies : fringe organizations and foot soldiers of Hindutva. -- New Delhi : Juggernaut, 2017. --229 S. -- ISBN 978-93-8622-824-6. -- S. 73. -- Fair use]
1.6.3. Hindu jagarana vedike [Kannada: ಹಿಂದು ಜಾಗರಣ ವೇದಿಕೆ], literally, National Volunteer Association for men to protect the Hindus

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Hindu jagarana vedike -- Kannada: ಹಿಂದು ಜಾಗರಣ ವೇದಿಕೆ |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | https://www.facebook.com/search/top/?q=Hindu+Jagarana+Vedike&init=public.
-- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 https://www.facebook.com/search/top/?q=%E0%B2%B0%E0%B2%BE%E0%B2%B7%E0%B3%8D%E0%B2%9F%E0%B3%8D%E0%B2%B0%E0%B3%80%E0%B2%AF+%E0%B2%B9%E0%B2%BF%E0%B2%82%E0%B2%A6%E0%B3%81+%E0%B2%9C%E0%B2%BE%E0%B2%97%E0%B2%B0%E0%B2%A3+%E0%B2%B5%E0%B3%87%E0%B2%A6%E0%B2%BF%E0%B2%95%E0%B3%86&init=public. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 (In Kannada) https://www.facebook.com/Hindu-Jagarana-Vedike-Karnataka-687802518001575/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
| Name | Dharma Jagran Samanvaya Vibhag - Sanskrit/Hindi: धर्म जागरण समन्वय विभाग / Dharma Jagran Samanvay Samiti - Sanskrit/Hindi: धर्म जागरण समन्वय समिति |
|---|---|
| Funktion | eine patriotische Botschaft an die Jugend zu schicken |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Mitglieder 2018 | 2000 Hauptamtliche |
| Gegründet | 1996 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | Bajrang Dal - Hindi: बजरंग दल |
| Webpräsenz |
http://dsvap.blogspot.de/. -- Zugriff am 208-02-21
https://www.facebook.com/VICHARKENDRA/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 https://www.facebook.com/Dharma-jagaran-samanvay-vibhag-Odisha-870681126276519/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
Über 50.000 Rekonvertierte in 5 Jahren
6.4. Dharm Jagaran Samiti, Organization for conversion of non-Hindus to Hinduism and their coordinating committee "Dharam Jagaran Samanvay Samiti"
Die Organisation ist vor allem beteiligt an Hasstiraden gegen Muslime, fordert Geburtenkontrolle für Muslime, will illegale Muslime aus Bangladesh zurückschicken, will den von Pakistan und China besetzten Teil von Kaschmir an Indien angliedern. Die Organisation beteiligt sich im Auftrag des RSS insbesondere an "ghar wapsi (Hindi: घर वापसी)" Programmen [Rekonversionen] von armen Leuten (Muslimen und Christen) zum Hinduismus, z.B. mit Angeboten von BPL-Karten [below-poverty-line identity cards], Aadhaar (आधार) Karten [Ausweis mit der nationalen Identifikationsnummer, mit der man u.a. verschiedene Dienste von Regierungsseite bekommen kann] und Geld. Aussage eines Mitglieds der Organisation nachdem er wegen der Konversion von 57 Muslim-Familien 2014 in Agra (आगरा) von der Polizei festgenommen wurde:
"we plan a series of programmes to create awareness among Hindus to prevent conversion and bring back converted Hindus to their parental religion".
Und:
"But we have been directed to be careful this time and avoid any controversy that can draw criticism for the Modi government."
[s. Verma, Lalmani: To give a boost to 'ghar wapsi', RSS appoints Dharma Jagran in-charge. - In The Indian Express. - 2015-04-03. http://indianexpress.com/article/lucknow/to-give-a-boost-to-ghar-wapsi-rss-appoints-dharma-jagran-in-charge/ -- Zugriff am 2016-09-12].
| Name | Muslim Rashtriya Manch [MRM] -- Hindi: मुस्लिम राष्ट्रीय मंच -- National Front of Muslims |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Organisation des RSS für indische Muslime. |
| Präsident 2018 | Indresh Kumar -- Hindi: इंद्रेश कुमार |
| Mitglieder | 10.000 Volunteers (2014) |
| Gegründet | 2002 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | RSS |
| Webpräsenz | http://muslimrashtriyamanch.org . -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 https://www.facebook.com/IndianNationalistMuslims/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Muslim_Rashtriya_Manch. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 |
6.5. Muslim Rashtriya Manch [Hindi: मुस्लिम राष्ट्रीय मंच], National Front of Muslims
Die Organisation wurde 2002 von einer Gruppe von nationalistischen Muslimen und Funktionären des RSS gegründet. Gemäß der Ideologie des RSS sind alle indischen Muslime Hindus, denn sie haben dieselben Vorfahren, Kultur und Tradition wie die Hindus; sie sind nicht von außen gekommen, also sind sie keine Minderheit. (Als Minderheiten werden Parsen, Juden und Anglo-Indians gesehen.) Das Ziel der Organisation ist, die Hindutva-Ideologie unter den indischen Muslimen zu verbreiten.
Der MRM unterstützt
Da Wohnviertel, in denen Muslime wohnen, von manchen Hindus als Klein-Pakistan bezeichnet werden (und die Bewohner als Pakistanis) hat der derzeitige [2017] Leiter des MRM muslimische religiöse Führer aufgefordert, dass sie Fatwas (فتوى) gegen die Personen aussprechen sollen, die auf indischem Boden pakistanische Flaggen hissen. [s. Homepage des MRM und: "Issue fatwas against those who unfurl Pakistani flags in India. - In Hindustan times. - Kindle ed. - 2017-06-20. - Zugriff am 2017-06-20]

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Rashtriya Sikh Sangh -- Hindi: राष्ट्रीय सिख संघ / Rashtriya Sikh Sangat -- Hindi: राष्ट्रीय सिख संगत -- Panjabi: ਰਾਸ਼੍ਟ੍ਰੀ ਸਿਖ ਸਂਗਤ |
|---|---|
| Funktion | für die Verbesserung der Beziehungen zwischen Sikhs (Panjabi: ਸਿੱਖੀ) und dem Rest der Hindugesellschaft |
| Präsident 2018 | Gurcharan Singh Gill |
| Gegründet | 1986 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | RSS |
| Webpräsenz |
https://www.facebook.com/rashtriyasikhsangatdli/. -- Zugriff am
2018-02-21
https://twitter.com/RshtrSikhSangat?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rashtriya_Sikh_Sangat. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 |
6.7. Rashtriya Sikh Sangat [Hindi: राष्ट्रीय सिख संगत], a sociocultural organisation with the aim to spread the knowledge of Gurbani [Punjabi: ਗੁਰਬਾਣੀ]to the Indian society

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Hindu Munnani -- Tamil: இந்து முன்னணி |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Organisation in Tamil Nadu (தமிழ் நாடு) zur Verteidigung des Hinduismus |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1981 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | RSS |
| Webpräsenz | http://hindumunnani.org.in -
nur in Tamil. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21. https://www.facebook.com/search/top/?q=Hindu+Munnani&init=public. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 https://twitter.com/hmrss1980?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hindu_Munnani / https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hindu_Munnani. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 |
6.8. Hindu Munnani [Tamil: இந்து முன்னணி], a religio-cultural organization based in Tamil Nadu.
Die Organisation wurde vom RSS gegründet. Aktueller Anlass waren 1981 die Konversionen von etwa 800 Dalits in Meenakshipuram (மீனாட்சிபுரம்) zum Islam. Die Dalits protestierten damit gegen die Kastendiskriminierung. Hindu Munnani kämpft seit der Zeit gegen islamische Gruppen und gegen Konversionen zum Christentum.
Als Aufgabe der Organisation wird u.a. angegeben:
Die Aktivitäten führten immer wieder zu Hindu-Muslim und Hindu-Christentum Aufständen mit Morden. Z.B. gab es 1998 während Lal Krishna Advanis (1927 - ) (Sindhi: لال کرشن اڈوانی) Wahlkampf in Coimbatore (Tamil: கோயம்புத்தூர) Bombenanschläge von islamischen extremistischen Gruppen mit etwa 60 Toten. Im September 2016 wurde der offizielle Sprecher der Hindutva-Gruppe C. Sasikumar getötet. Man befürchtet, dass die Situation in Tamil Nadu (தமிழ் நாடு) so werden könnte wie die in Gujarat (ગુજરાત) 2002 [vgl. Violence erupts in Coimbatore after mobs protest murder of Hindu Munnani leader. - In: Hindustan times. - Kindle ed. - 2016-09-24][zu Hindu Munnani: vgl.: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hindu_Munnani#Activities -- Zugriff am 2016-09-27
1.6.8. Hindu Rashtra Sena [Hindi: हिंदू राष्ट्रसेना], propagating for the establishment of Hindu Rashtra.

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Hindu Rashtra Sena -- Hindi: हिंदू राष्ट्रसेना |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | Dhananjay Desai |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | https://www.facebook.com/search/top/?q=Hindu+Rashtra+Sena&init=public.
-- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 https://www.facebook.com/hrsag/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
1.6.9. Hindu Aikya Vedi [Malayalam: ഹിന്ദു ഐക്യവേദി] , Hindu United Front based in Kerala

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Hindu Aikya Vedi -- Malayalam: ഹിന്ദു ഐക്യവേദി -- Hindu United Front |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | K.P.Sasikala Teacher -- Malayalam: ടി.പി.ചന്ദ്രശേഖരൻ ആദ്യഇരയോ |
| Gegründet | 1992 |
| Hauptquartier | Thiruvananthapuram (Malayalam: തിരുവനന്തപുരം) |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.hinduaikyavedi.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hindu_Aikya_Vedi. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 |
1.7.1. Ekal Vidyalaya [Hindi: एकल विद्यालय], Involved in free education and village development in rural areas and tribal villages of India.

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Ekal Vidyalaya -- Hindi: एकल विद्यालय |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "to bring basic education to every child across rural India" (https://www.ekal.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | Jitendra Bhai Bhansali |
| Gegründet | 1989 |
| Hauptquartier | New Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
https://www.ekal.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21
https://www.facebook.com/Ekal.Vidyalaya/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/EkalVidyalaya?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Vidya Bharati Akhil Bharatiya Shiksha Sansthan [Vidya Bharati] -- Hindi: विद्या भारती अखिल भारतीय शिक्षा संस्थान - विद्या भारती |
|---|---|
| Funktion | für die Erziehung zuständige Organisation (NGO) des RSS. |
| Präsident 2018 | Govind Pd. Sharma |
| Gegründet | 1952/1977 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | RSS |
| Webpräsenz | http://vidyabharti.net/ - Zugriff
am 2018-02-21. https://twitter.com/VidyaBharti19?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vidya_Bharati. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 |
7.3. Vidya Bharati [विद्या भारती], Educational Institutes
Es handelt sich um eine Nicht-Regierungsorganisation, die eines der größten privaten Netzwerke von Schulen für Hindu-Kinder in Indien betreibt. Die Einrichtungen haben verschiedene Namen: u.a.
Es begann 1952 in Gorakhpur (Hindi: Hindi: गोरखपुर) mit der Schule Saraswati Shishu Mandir (Hindi: सरस्वती शिशु मंदिर). Die Schulen sollen Missionsschulen und "sogenannte öffentliche Schulen" ersetzen. Die Organisation wird in den Staaten, die von der BJP regiert werden, besonders unterstützt. Es werden neben den vom Staat vorgeschriebenen Lehrbüchern Lehrbücher mit Hindutva-Ideologie benutzt. Zusätzlich Unterrichtsfächer sind:
Mädchen sollen zu guten Hausfrauen und Müttern erzogen werden, also lernen sie u.a. auch kochen.
Vidya Bharati ist vor allem auch in ländlichen Gebieten tätig: 6219 Schulen in Dörfern, 583 in unterprivilegierten Orten und 830 in Stammesgebieten. "
The effort is to foster national unity, respect for all religions & Faiths, patriotism & pride in Bharatiya Dharma & Sanskriti through the medium of education."
[Quelle: http://vidyabharati.net/edu_beliefs.php - Zugriff am 2017-01-04]
Für 2012 und 2013 wird für die gesamte "Formal Education" (also Vorschule, Grundschule usw.) die Anzahl mit 13.514 angegeben. Für die "Informal Education, nämlich Sanskar Kendras (Hindi: संस्कार केन्द्र) und Einlehrer-Schulen wird 9.806 angegeben [http://vidyabharati.net/statistics.php. - Zugriff am 2017-01-04]
Die Organisation will ein nationales Erziehungssystem entwickeln, das eine Generation von jungen Männern und Frauen bilden soll, die sich für Hindutva verpflichten und durchdrungen sind mit patriotischem Fieber usw. [s. http://vidyabharati.net/philosphy_aim.php - Zugriff am 2017-01-04]
1.7.2.1. Saraswati Shishu Mandir (सरस्वती शिशु मंदिर), Nursery

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Saraswati Shishu Mandir -- Hindi: सरस्वती शिशु मंदिर |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1952 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | RSS/Vidya Bharati |
| Webpräsenz | https://www.facebook.com/saraswatishishumandir.school/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 |
| Wikipedia | https://hi.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E0%A4%B8%E0%A4%B0%E0%A4%B8%E0%A5%8D%E0%A4%B5%E0%A4%A4%E0%A5%80_%E0%A4%B6%E0%A4%BF%E0%A4%B6%E0%A5%81_%E0%A4%AE%E0%A4%82%E0%A4%A6%E0%A4%BF%E0%A4%B0. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 (Hindi) |

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Vijnana Bharati [VIBHA] -- Hindi: विज्ञान भारती - विभा |
|---|---|
| Funktion | zuständig für Wissenschaft und Technologie innerhalb von RSS. |
| Präsident 2018 | Vijay P. Bhatkar (Marathi: विजय पांडुरंग भटकर, 1946 - ) |
| Gegründet | 1991 |
| Hauptquartier | New Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | RSS |
| Webpräsenz | http://vibhaindia.org/
-- Zugriff am 2016-11-23 https://www.facebook.com/Vijnana-Bharati-175906902501258/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vijnana_Bharati. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 |
7.4. Vijnana Bharati, Science Forum
VIBHA bezeichnet sich als eine Bewegung für "Swadeshi" [Sanskrit/Hindi: स्वदेशी] - Wissenschaften im Geist des "Swadeshi". Die Organisation setzt sich ein für die Entwicklung Indiens durch Anwendung von Wissenschaft und Technologie in allen möglichen Bereichen. Dazu nutzt VIBHA 27 unabhängige Organisationen in Indien.
VIBHA wurde offiziell 1991 in Nagpur (नागपूर) als eine "professional cum popular" Bewegung im Feld der Wissenschaft und Technologie begründet. Vorläufer war in den 80er Jahren eine Bewegung im Indian Institute of Science in Bengaluru (ಬೆಂಗಳೂರು) unter der Leitung von K. I. Vasu. [Quelle: Homepage]. VIBHA hat die Aufgabe, nachzuweisen, dass es in der Wissenschaft nichts gibt, was nicht schon im alten Indien bekannt war. Beispiele:
"Astronomy and metaphysics are described in the Rig Veda [Sanskrit: ऋग्वेद], the concept of the atom can be traced to Vedic times, Paramanu [Sanskrit: परमाणु] (beyond atom) was considered to be the smallest particle, which cannot be divided further, nuclear energy is produced by splitting the same. Sushruta [Sanskrit: सुश्रुत,] is the `father of surgery´ who described over 300 surgical procedures ... including a method of stitching intestines by using `ant-heads as stitching material´".
[Quelle: Govt should stop RSS from furthering its ideological agenda in schools. In: Hindustan times. - Kindle ed. - 2016-11-17] [Aktuelles s. unter 5.4]

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Akhil Bharatiya Vanvasi Kalyan Ashram -- Hindi:
अखिल भारतीय वनवासी कल्याण आश्रम Späterer Name: Vanavasi Kalyan Ashram -- Hindi: वनवासी कल्याण आश्रम |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Organisation für Stammesbevölkerung (Adivasi [Sanskrit/Hindi: आदिवासी] / Vanvasi [Sanskrit/Hindi: वनवासी]) |
| Präsident 2018 | Jagdeo Ram Oram |
| Gegründet | 1952 |
| Hauptquartier | Jashpurnagar -- Hindi: जशपुर नगर |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.kalyanashram.org/.
-- Zugriff am 2018-02-21. letzte eigene Webpräsenz 2016: https://web.archive.org/web/20131030140806/http://kalyanashram.in/ -- Zugriff 2017-06-23. https://www.facebook.com/Vanvasi/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vanavasi_Kalyan_Ashram. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-21 |
8.1. Vanavasi Kalyan Ashram [Hindi: अखिल भारतीय वनवासी कल्याण आश्रम], Organisation for the improvement of tribals
Dieser Ashram wurde 1952 gegründet. Es ging vor allem darum, den Einfluss der christlichen Missionare auf die Stammesbevölkerung einzuschränken.
1.8.2. Youth for seva

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Youth for seva (YFS) |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "a nation-wide volunteering movement that inspires youth to volunteer, and provides them with meaningful opportunities to serve the community." (https://youthforseva.org/about-us/. -- Zugriff am 2019-02-22) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | D. M. Kiran |
| Gegründet | 2007 |
| Hauptquartier | Konanakunte, Bengaluru (Kannada: ಕೋಣನಕುಂಟೆ, ಬೆಂಗಳೂರು) |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
https://youthforseva.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 https://www.facebook.com/YouthForSevaOfficial/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/yfs_official?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
Abb.: Präsenz von Youth for Seva in Indien
[Bildquelle:
https://youthforseva.org/about-us/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22. -- Fair use]
1.8.3. Friends of Tribals Society (FTS) -- Vanbandhu Parishad (वनबंधु परिषद)

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Friends of Tribals Society -- Vanbandhu Parishad Hindi: वनबंधु परिषद |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "Empowerment of crores of Tribals and Rural brethren of Bharat by making them socially strong educationally aware and economically vibrant and self-reliant so that with their involvement the Mother Bharat reaches the pinnacle of glory." (http://www.ftsindia.com/vision-mission/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | Sajan Kumar Bansal |
| Gegründet | 1989 |
| Hauptquartier | Kolkata (Bengali: কলকাতা) |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.ftsindia.com/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22. |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Friends_of_Tribals_Society. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
As on September 30, 2016 FTS was funding and monitoring 29463 one teacher schools in 18 states. FTS along with other associates were running 54388 one teacher schools in India and Nepal.
1.8.4. Anusuchit Jati-Jamati Arakshan Bachao Parishad, Organisation for the improvement of Dalits
| Name | Anusuchit Jati-Jamati Arakshan Bachao Parishad |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
1.8.5. Bharat-Tibet Maitri Sangh (भारत तिब्बत मैत्री संघ), India Tibet Friendship Society
| Name | Bharat-Tibet Maitri Sangh -- Hindi: भारत तिब्बत मैत्री संघ -- India Tibet Friendship Society (ITFS) |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | Satya Prakash Malviya |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | New Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://www.indiatibet.com/%E0%A4%AD%E0%A4%BE%E0%A4%B0%E0%A4%A4-%E0%A4%A4%E0%A4%BF%E0%A4%AC%E0%A5%8D%E0%A4%AC%E0%A4%A4-%E0%A4%AE%E0%A5%88%E0%A4%A4%E0%A5%8D%E0%A4%B0%E0%A5%80-%E0%A4%B8%E0%A4%82%E0%A4%98/.
-- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 https://www.facebook.com/India-Tibet-Friendship-Society-1767424436877579/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
1.9.1. Organiser, Magazine

Abb.: ©Balken
[Fair use]
| Name | Organiser |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Wochenzeitschrift |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1947 |
| Hauptquartier | New Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://www.organiser.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22
https://www.facebook.com/eOrganiser/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Organiser_(magazine). -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
"ORGANISER, one of the oldest and most widely circulated weeklies from the capital, first hit the stands in 1947, a few weeks before Partition, Edited and enriched by eminent personalities like
- A.R. Nair,
- K.R. Malkani,
- L.K. Advani,
- V.P. Bhatia,
- Seshadri Chari,
- R. Balashanker and
- now Prafulla Ketkar (Email: editor.organiser@bpdl.in)
to name but a few, ORGANISER has come to believe that resistance to tyranny is obeisance to God.
REPEATED attempts to muffle its voice and the motivated opposition to it by some powers did not succeed..
GURUJI Golwalkar (the second Sarsanghchalak of Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh) once said: "For clear, straightforward, impartial views on subjects of national and international importance and for imbibing unadulterated patriotism, it is useful to read ORGANISER. It will fulfil the expectations for correct guidance in all current affairs.
A strong bond of commitment has continued to contribute to the growth and popularity of ORGANISER on the part of the right thinking public, carving out a niche for itself in national life.
NOT a small number of thinkers, writers, opinion-makers, legislators, members of both the Houses of Parliament, editors of dailies and other periodicals with a countrywide circulation are regular readers of ORGANISER."
[Quelle: http://www.organiser.org/static/about.aspx. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-28. -- Fair use]
1.9.2. Vishwa Samvada Kendra (VSK) -- विश्व संवाद केन्द्र, communication Wing, spread all over India for media related work, having a team of IT professionals (samvada.org)

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Vishwa Samvada Kendra (VSK) -- Hindi/Sanskrit: विश्व संवाद केन्द्र |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Official Media Centre of Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh, (RSS) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | Rajesh Padmar |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | Bangalore (Kannada: ಬೆಂಗಳೂರು) |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://samvada.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22
https://www.facebook.com/samvada/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 https://twitter.com/vishwa_samvad?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
1.9.3. Hindustan Samachar -- हिन्दुस्तान समाचार, a multi-lingual news agency.

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Hindustan Samachar -- Hindi: हिन्दुस्तान समाचार |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Nachrichtenagentur |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1948 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://www.hindusthansamachar.in/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 (in
Hindi) https://www.facebook.com/hindustansamachar1/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 https://twitter.com/news_hs?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hindustan_Samachar. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
1.10.1. Bharatiya Vichar Kendra (BVK) (भारतीय विचार केंद्रम्)

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Bharatiya Vichar Kendra (BVK) -- Sanskrit: भारतीय विचार केंद्रम् |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Kulturinstitut "Vichara Kendram addresses itself to a detailed study of the multi-dimensional achievements of India with a view to substantiat their validity in the present context. " (http://www.vicharakendram.org/bvk/about-bvk. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Präsident 2018 | P. Parameswaran (Malayalam: പി. പരമേശ്വരൻ, 1927 - ) (siehe: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/P._Parameswaran. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22) |
| Gegründet | 1982 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.vicharakendram.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
10.1. Bharatiya Vichara Kendra, General Think Tank.

Abb.: P. Parameswaran (Malayalam: പി. പരമേശ്വരൻ, 1927 - ), 2011
[Bildquelle: Vibitha vijay/Wikimedia. --
CC BY-SA
3.0]
1.10.2. Hindu Vivek Kendra -- हिन्दू विवेक केन्द्र, a resource center for the promotion of the ideology of Hindutva.

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Hindu Vivek Kendra -- Hindi: हिन्दू विवेक केन्द्र |
|---|---|
| Funktion | a resource center for
the promotion of Hindutva. "The ideology of Hindutva is becoming popular because there is a growing realization that everything else that has been tried to inculcate a national spirit, has failed to yield the desired results. Many people previously opposed to Hindutva have embraced the ideology, as they believe that the solutions to the country's problems can be found within it." (http://www.hvk.org/about.html. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | Mumbai (Marathi: मुंबई) |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://www.hvk.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22
https://twitter.com/HinduVivekKendr. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hindu_Vivek_Kendra. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22. |

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Vivekananda Kendra -- Hindi: विवेकानन्द केन्द्र -- Tamil: விவேகானந்த கேந்திரம் |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Entwicklungshilfe bei
Stammesbevölkerung "(1) Transforming our people's inherent God-wardness into the right spiritual urge rising out of the teachings of the Upanishads, namely,
(2) To convert the spiritual fervour thus
released into works of national reconstruction. " |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | Kanyakumari (Tamil: கன்னியாகுமரி) |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://www.vivekanandakendra.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22. https://twitter.com/vkendra?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vivekananda_Kendra. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
10.3. Vivekananda Kendra [Tamil: விவேகானந்த கேந்திரம்], promotion of Swami Vivekananda's ideas with Vivekananda International Foundation in New Delhi as a "Public Policy Think Tank" with 6 Centres of study.
Abb.: Vivekananda Kendras
[Bildquelle: ©Google Maps /
http://www.vivekanandakendra.org/vivekananda-kendra-centers. -- Fair use]
1.10.4. India Policy Foundation (भारत नीति प्रतिष्ठान), a not-for-profit Think Tank

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | India Policy Foundation -- Hindi: भारत नीति प्रतिष्ठान |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "non-profit Think Tank dedicated to exploring constructive solutions to contemporary problems through its intellectual pursuits, a platform for eminent personalities of all walks of life to come together, discuss and debate, paving the way for a consensus on public policies in line with India’s rich philosophical content and intellectual legacies." (http://www.indiapolicyfoundation.org/encyc/2014/7/5/About-India-Policy-Foundation.aspx#.Wo_sBucxlPY. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | Kapil Kapoor |
| Gegründet | 2008 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://www.indiapolicyfoundation.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 https://www.facebook.com/IndiaPolicyFoundation/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | --- |

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Bharatiya Shikshan Mandal -- Hindi: भारतीय शिक्षण मंडल |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Organisation
zur Unterstützung nationaler Erziehung "The goal of the education should be ' The holistic personality development of students in the context of the national resurgence. Indian culture should be reflected from the personality of the students. All the members of the teaching fraternity such as the teachers, the administrators of the alma-maters, and the parents should get involved in this activity. We do not need to perform the task of reconstruction of the Rashtra, only reawakening is needed." (http://bsmbharat.org/Encyc/2015/2/12/1189687.aspx#.Wo_uGOcxlPY. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-23) |
| Präsident 2018 | Sachchidananda Joshi |
| Gegründet | 1969 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://www.bsmbharat.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 https://www.facebook.com/bsmbharat/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-24 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
10.5. Bharatiya Shikshan Mandal, a Think Tank on educational reforms
Die Organisation begann 1969 im Bereich der Erziehung zu arbeiten. Sie hat 268 Zweigstellen in 24 Staaten (Stand Juni 2017). Es geht darum das Erziehungssystem zu indisieren.
So wurde z.B. im Februar 2017 eine internationale Konferenz mit dem Thema "Idea of Bharat" abgehalten. Unter den 500 Teilnehmern vor allem aus Universitäten waren auch hochrangige Politiker wie Nitin Gadkari (Hindi: नितिन गडकरी, 1957 - ) und der indische Präsident Pranab Mukherjee (Bengali: রনব কুমার মুখার্জী, 1935 - ). Aus dem Bericht:
"The concept that emerged through this conference shed light on the essence of being Bharatiya [भारतीय] and how it is beneficial for the whole world. Humanity is craving for a solution to the existential problems like terrorism, global warming, climate change and economic meltdown. In this era of crisis, a permanent solution can be achieved by following Bharatiya way of life. [... Die Konferenz...] is a beacon of light to guide the youth and the people of this country in the right direction, based on eternal Dharmic principles."
Der Bericht schließt mit:
भारत माता की जय! वन्दे मातरम्! [Hindi]
"Bharat Mata Ki Jai! Vande Mataram!"
[Sieg für Mutter Indien! Ich grüße die Mutter][s. Scholars meet declares to implement the 'Idea of Bharat' in educational institutes. - http://bsmbharat.org/Encyc/2017/3/2/Scholars-meet-declares-to-implement-the-%E2%80%9CIdea-of-Bharat%E2%80%9D-in-educational-institutes.aspx#.WU_OIWhCSUk]
1.10.6. India Foundation, a Think Tank

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | India Foundation |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | New Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://www.indiafoundation.in/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 https://twitter.com/indfoundation?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCoa562Q8QrgTAAyqNsx36oA. -- Zugriff am 2019-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
"India Foundation is an independent research centre focussed on the issues, challenges and opportunities of the Indian polity. The Foundation believes in understanding contemporary India and its global context through a civilizational lens of a society on the forward move. Based on the principles of independence, objectivity and academic rigour, the Foundation aims at increasing awareness and advocating its views on issues of both national and international importance. It seeks to articulate Indian nationalistic perspective on issues. India Foundation’s vision is to be a premier think tank that can help understand the Indian civilizational influence on our contemporary society. With a team of dedicated professionals based at its office in New Delhi, the Foundation works with partners and associates both in India and overseas to further its stated objectives."
[Quelle: http://www.indiafoundation.in/about-india-foundation/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22]

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Akhil Bharatiya Itihas Sankalan Yojana [ABISY] [Akila Bharateeya Itihasa Sankalana Yojana] -- Hindi: अखिल भारतीय इतिहास-संकलन योजना -- All-India history reform project |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Organisation des RSS, deren Aufgabe es ist, die indische Geschichte aus einer nationalen Perspektive zu schreiben. |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1978 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | RSS |
| Webpräsenz | http://itihasabharati.org/ -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22. |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Akhil_Bharatiya_Itihas_Sankalan_Yojana. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
10.7. Akhil Bharatiya Itihas Sankalan Yojana (ABISY) [Hindi: अखिल भारतीय इतिहास-संकलन योजना], All-India history reform project
"The objective of Akila Bharatheeya Itihasa Sankalana Yojana (ABISY) is to write Bharatheeya history from a national perspective.
The British distorted Bharatheeya history; destroyed / perverted the tradition, heroes, culture, literature and language. Hence ABISY coordinates patriotic, bold and incorruptible scholars & historians to write history truthfully on the basis of facts and evidences.
In order to systematically compile all available facts comprehensively, regional chapters of ABISY have been established throughout the country. The regional chapters are functioning under the name “Bharatheeya Itihasa Sankalana Samithi (BISS) [भारतीय इतिहास-संकलन समिति]”.
Akila Bharatheeya Itihasa Sankalana Yojana is actively involved in bringing out the history of Bharath for the past 5000 years ie from 3102 BC, the beginning of kaliyuga onwards."[Quelle: http://itihasabharati.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22. -- Fair use]
Die Organisation wurde von 1978 von Moro Panth Pingle [Moropant Pingley] (Hindi: मोरोपंत पिंगले, 1919 - 2003), ein Pracharak (प्रचारक) des RSS, der auch für die Zerstörung der Babri Moschee (بابری مسجد) in Ayodhya (अयोध्या) verantwortlich war, begründet. Um Daten besser ermitteln zu können, hat die Organisation regionale Untergruppen unter dem Namen Bharateeya Itihasa Sankalana Samithi [BISS] (भारतीय इतिहास-संकलन समिति). eingerichtet. Die Organisation geht davon aus, dass die indische Geschichte durch die Briten verfälscht wurde: die Tradition, Helden, Kultur, Literatur und Sprache seien zerstört und pervertiert worden. Also muss die Geschichte Indiens der vergangenen 5000 Jahre, beginnend mit dem Jahr 3102 BC (Anfang des Kaliyuga [Sanskrit: कलियुग]) neu geschrieben werden. Laut ABISY sind die Arier nicht nach Indien eingewandert, sondern von dort in die ganze Welt ausgewandert:
"“Arya” means superior, intelligent, refined and cultured. Archeological investigations and DNA studies by the scientists have proved that no outsiders came to Bharath in ancient times; In contrary, Indians have immigrated to the entire world and spread their knowledge, culture and contributed for their growth."
[http://itihasabharati.org/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=101&Itemid=120 -- Zugriff 2017-10-31].
Ein großes Projekt, das von der Modi-Regierung
durchgeführt wird, ist die Ausgrabung des mythischen Flusses Saraswati
[Sanskrit: सरस्वती],
der in den Vedas beschrieben wird. ABISY behauptet, dass man den Lauf
des Flusses gefunden, an dessen Ufern sich die Städte der Harappa-Kultur befunden haben, und dass der Fluss vor 4000 Jahren ausgetrocknet
sei. Also müsste der Rigveda [Sanskrit: ऋग्वेद] wesentlich älter sein als in der heutigen
Wissenschaft (zwischen 1500 und 1200 v. Chr.) angenommen wird.
1.10.8. Syama Prasad Mookerjee Research Foundation (SPMRF)

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Syama Prasad Mookerjee Research Foundation (SPMRF) |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | Ram Lal |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | New Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://www.spmrf.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22
https://www.facebook.com/spmrfoundation/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 https://twitter.com/spmrfoundation?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | --- |

Abb.: Syama Prasad Mookerjee [Bengali:
শ্যামাপ্রসাদ মুখোপাধ্যায়,
1901 - 1953]
[Bildquelle:
https://www.sabrangindia.in/article/syama-prasad-mookerjee-how-selfless%E2%80%99-was-patriot%E2%80%99.
-- Zugriff am 2018-02-22. -- Vermutlich piblic domain, sonst fair use]
"Dr. Syama Prasad Mookerjee Research Foundation (SPMRF) has emerged as a forum which facilitates the convergence of ideas, positions and visions that aspire to strengthen the nation and preserve her unity and integrity and contribute towards her progress and integral development. Committed to the nationalist ideological vision and thoughts of Dr. Syama Prasad Mookerjee [Bengali: শ্যামাপ্রসাদ মুখোপাধ্যায়, 1901 - 1953] and Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay [Hindi: दीनदयाल उपाध्याय], SPMRF strives to strengthen and to uphold issues and positions in tune with India’s national interest. It aims to identify the multifarious challenges before the nation and the people and attempts to bring about a greater awareness of these among a wider cross-section of our people. It aims to do this through analysing, examining and studying, not only the present context of the challenges, but also their historical and civilisational backdrop. The principal area of the Foundation’s focus is to create an intellectual ambience where nationalist thought and nationalism can find free expression. Through research, publications, advocacy, debates, discussions and round-tables, the Foundation aims to highlight issues that are crucial in the national interest. A wide number of experts have, over a period, lent their support, expertise and insight to such an effort. National resurgence, cultural rejuvenation, national integration and national self-reliance are the ideals which SPMRF espouses and strives to work for.
SPMRF provides a platform for experts, practitioners, academics and other opinion makers to come together and exchange ideas, evolve positions on a wide range of issues facing the nation with the objective of educating a wider public opinion. In order to encourage the study and dissemination of the work and legacy of Dr. Syama Prasad Mookerjee – educationist, statesman and founder of the Bharatiya Jan Sangh, the mother political organisation of the Bharatiya Janata Party – SPMRF has also undertaken research on his life and work by bringing out new facets which can inspire youth to dedicate themselves for national progress and for working to uphold and sustain the grand vision of “One India” and “Great India.”
It is to realise this vision of national cohesion, unity and oneness that SPMRF invites all to make a positive effort and to contribute their best thoughts and achievements that may lead India to greater pinnacles of glory and strength."
[Quelle: http://www.spmrf.org/spmrf/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22. -- Fair uuse]

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Hindu Swayamsevak Sangh -- Hindi: हिन्दू स्वयंसेवक संघ -- Hindu Volunteer Association |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Auslandorganisation des Sangh Parivar - संघ परिवार |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1947 in Kenya |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | Sangh Parivar - संघ परिवार |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.hssworld.org/ -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22. |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hindu_Swayamsevak_Sangh. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
11.1. Hindu Swayamsevak Sangh [Hindi: हिन्दू स्वयंसेवक संघ], literally, Hindu Volunteer Association overseas wing of RSS
Established in 1940s in Kenya, it is at present dynamic in 34 nations and brags 570 branches.
In Ländern wie z.B. Kenia, Nepal, Australien, USA, in denen viele Inder bzw. Indischstämmige leben, ist der Sangh unter dem Namen HSS vertreten. Die jeweilige Organisation entspricht der Struktur und den Aktivitäten des indischen RSS und dessen Ideologie.
Eine der ältesten dieser Organisationen ist die in Großbritannien:

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Hindu Swayamsevak Sangh UK [HSS UK] |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "to advance Hindu religion and to educate the public in the Hindu ideals and way of life" |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1966 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | http://hssuk.org/ -- Zugriff am
2018-02-22 https://www.facebook.com/hssuk/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 https://twitter.com/hss_uk?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
Motto auf der Homepage "Sanskār, Sewā, Sangathan" (Hindi: संस्कार सेवा संगठन) (Hindu-Werte und Verhaltensweisen, Dienst, Organisation)
1974 wurde HSS als Wohltätigkeitsorganisation in Großbritannien anerkannt.
Als Zweck wird genannt
"to advance Hindu religion and to educate the public in the Hindu ideals and way of life".
Gegenüber der Charity Commission England and Wales gibt HSS an, dass der RSS keine Kontrolle ausübt. HSS bezeichnet sich als nationale Organisation, die mehr als 110 shakhas (Hindi: शाखा) in Großbritannien hat. Die Charity Commission führte eine Untersuchung durch, weil ein Sprecher des HSS in einer öffentlichen Veranstaltung des HSS für Kinder islam-feindliche Kommentare abgegeben hat (Die Rede wurde im Januar 2015 im Fernsehen gezeigt. [vgl. UK regulator raps Hindu Swayamsevak Sangh for anti-Islamic remarks. - In: Hindustan times. - Kindle ed. - 2016-09-03]).
Zum HSS UK gehören:
| Name | Hindu Sevika Samiti |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Organisation des HSS UK für Mädchen und Frauen |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | HSS UK |
| Webpräsenz | http://hssuk.org/samiti/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
Organisation des HSS UK für Mädchen und Frauen, die universale Hindu-Werte lernen, praktizieren und bewahren sollen. ...
"to build self-confidence, cultivate a sense of social consciousness and archieve all round development in order to fase the challenges and rigours of the modern era."
[Quelle: http://hssuk.org/samiti/ -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22].
Dazu gehören Übungen zur Verteidigung und Yoga-Übungen.

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Balagokulam |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Organisation des HSS UK für Kinder |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | HSS UK |
| Webpräsenz | http://hssuk.org/balagokulam/ -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
Gokulam/Gokul (Hindi: गोकुल) ist der angebliche Ort, an dem Krishna seine Kindheit verbracht hat.
Abb.: Lage von Gokul (Hindi: गोकुल)
[Bildquelle: © OpenStreetMap-Mitwirkende. --
CC BY-SA 2.0]
| Name | Hindu Sahitya Kendra [Hindu Literature Centre] |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Angebot von Materialien (Bücher, Zeitschriften, Audiomaterialien usw.) zur Kultur der Hindus. |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | HSS UK |
| Webpräsenz | http://hssuk.org/hindu-sahitya-kendra/ -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
HSK - eine Organisation des HSS UK - will das Interesse bezüglich der Hindus wecken und stärken. Es geht um das Angebot von Materialien (Bücher, Zeitschriften, Audiomaterialien usw.) zur Kultur der Hindus.

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Hindu Swayamsevak Sangh USA [HSS USA] |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1989 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://www.hssus.org/ -- Zugriff am
2018-02-22 https://www.facebook.com/hssus/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
HSS USA wurde 1989 gegründet und hat heute über 140 Shakhas (Hindi: शाखा) (weekly meeting centers) für Männer und Frauen im ganzen Land [s. http://www.hssus.org/content/view/18/112/ -- Zugriff am 2016-09-09]. In den USA leben etwa 2 Millionen Hindus.
Auch in den USA gibt es die Organisation Balagokulam [http://www.balagokulam.org/ ] für Kinder.
Insbesondere für den akademischen Bereich gibt es die Hindu Education Foundation.
[Zusammenstellung hauptsächlich nach: http://members.tripod.com/antibjp/archives/rss.html. -- Zugriff am 2016-07-28]
1.11.2. Hindu Students Council (HSC), Overseas Hindu Students' Wing

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Hindu Students Council |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Organisation von Hindu Studenten in USA und Kanada |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1990 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | Sangh Parivar |
| Webpräsenz | https://hindustudentscouncil.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hindu_Students_Council. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
1.12.1. Balagokulam (ബാലഗോകുലം / बालगोकुलम), To develop cultural consciousness in children

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Balagokulam -- Malayalam: ബാലഗോകുലം -- Hindi: बालगोकुलम |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1981 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | https://www.balagokulam.net/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Balagokulam. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
"Gokul is the place where an ordinary cowherd boy blossomed in to a divine incarnation. It is here that Krishna's magical days of childhood were spent and his powers came to be recognized. Every child has that spark of divinity within. BalaGokulam is a forum for providing the opportunity to children to discover and manifest that divinity. The program has been designed to enable children to appreciate their cultural roots, learn our ancient values in an enjoyable manner and also develop a sense of Sewa, Service to humankind.
Children will have lots of fun while they learn. Activities are planned for their physical, intellectual, social and spiritual development. Weekly activities include: Games, Yoga, Stories, Patriotic/Devotional Songs, Shlokas, Arts and Crafts. The syllabus also includes introducing children to some very fundamental pillars of Hindu Dharma including scriptures, symbolism, values & concepts; using stories and various other self-learning, experiential and exploratory methods.
All the BalaGokulam sessions are conducted absolutely free by team of dedicated & passionate volunteers."
[Quelle: https://www.balagokulam.net/about-us. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22. -- Fair use]
Siehe:
Balagokulam Guide. -- Online: http://www.balagokulam.org/teach/bgguide.pdf. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22
1.13.1. Samskrita Bharati [Sanskrit: संस्कृतभारती], promotion of the Sanskrit language

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Samskrita Bharati - Sanskrit: संस्कृतभारती |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "Promote the study of Samskrit and make it accessible to all sections of society." (https://samskritabharati.in/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 ) |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1981 |
| Hauptquartier | New Delhi |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | https://samskritabharati.in/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
1.13.2. Central Hindu Military Education Society, to encourage more Hindus to join the Defence Services

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Central Hindu Military Education Society |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1937 |
| Hauptquartier | Nashik (Marathi: नाशिक) |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://www.bhonsala.in/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 https://www.facebook.com/Central-Hindu-Military-Education-Society-1218175091543052/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bhonsala_Military_School. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
1.13.3. Kreeda Bharati (क्रीडा भारती), Sports Organization.
| Name | Kreeda Bharati -- Hindi: क्रीडा भारती |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Anzahl der Mitglieder | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | Pune (Marathi: पुणे) |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://kreedabharati.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 https://twitter.com/kreedabharati?lang=de. -- Zugriff am 2019-02-22 https://www.facebook.com/kridabharati/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | --- |

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Samskar Bharti -- Hindi: संस्कार भारती |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Künstlerorganisation |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1981 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://sanskarbharti.in/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22
https://www.facebook.com/search/top/?q=Samskar+Bharati&init=public. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
13.4. Samskar Bharati [Hindi: संस्कार भारती], Cultural unit
[Quelle der Übersicht: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sangh_Parivar#Sangh_Parivar_members. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-16]
| Name | Dharma Jagran Manch - Hindi: धर्म जागरण मंच |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Männerorganisation der Vishva Hindu Parishad Verhinderung von Konversionen von Hindus zu anderen Religionen bzw. die Rekonversion von Muslimen und Christen zu Hindus |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 2012 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | Vishva Hindu Parishad |
| Webpräsenz |
http://dharmjagran.org/ - - Zugriff am 2016-09-13. (überwiegend in Hindi)
(2018-02-22: Zugriff verweigert)
https://www.facebook.com/dharmjagranmanch/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | --- |
Die Gruppe kämpft insbesondere gegen den sog. Love jihad: muslimische Männer heiraten Hindu-Frauen, um sie zum Islam zu bekehren, und die Zahl der Muslime entsprechend zu erhöhen. So sind z.B. die Mitglieder der Organisation aufgefordert, Hindu-Mädchen Rakhis (Hindi: राखी) zu geben
"requesting them not to fell prey to such youths who lure them to convert their religion".
Ein Rakhi ist meistens ein geknüpftes Armband, das in indischer Tradition der Bruder der Schwester (oder auch weitere Verwandte oder Freunde) schenkt und damit eine schützende Verbindung entsteht.
[Vgl.: Verma, Lalmani: RSS wing launches rakhi crusade against 'love jihad'. - In: The Indian Express. - 2014-08-11. - http://indianexpress.com/article/lucknow/rss-wing-launches-rakhi-crusade-against-love-jihad/ -- Zugriff am 2016-09-13].
| Name | Rashtriya Suraksha Samiti -- Hindi: राष्ट्रीय सुरक्षा समिति |
|---|---|
| Funktion | gegen Sezessionismus im Punjab (Panjabi: ਪੰਜਾਬ) |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | https://www.facebook.com/pages/Rashtriya-Suraksha-Samiti/596983907007783. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 (keine Einträge!() |
| Wikipedia | --- |

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Akhil Bharatiya Hindumahasabha Hindi: अखिल भारतीय हिन्दू महासभा) |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 1915 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://abhm.org.in/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22
https://www.facebook.com/search/top/?q=Akhil+Bharat+Hindu+Mahasabha&init=public. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Akhil_Bharatiya_Hindu_Mahasabha. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
Hindu Mahasabha [Akhil Bharat Hindumahasabha (Hindi: अखिल भारतीय हिन्दू महासभा)]:
Ist eine der ältesten hindunationalistischen Organisationen, gegründet 1907, seit 1915 auf ganz Indien bezogen.
"Hindu Mahasabha is a hindusangathan (Hindi: संगठन) movement and politics of hindutva (हिन्दुत्व). Hindu Mahasabha is a non-secular party, established for safeguarding issues of Hindus" [s. Homepage].
Zu den aktiven Mitgliedern gehörte u.a. Vinayak Damodar Savarkar (Marathi: विनायक दामोदर सावरकर, 1883 - 1966), der Verfasser des für die Hindutva-Ideologie wichtigsten Textes "Hindutva : Who is a Hindu?", veröffentlicht 1923.

Abb.: Rückseite des Titelblatts der Ausgabe 1969
Keshav Baliram Hedgewar (Marathi: केशव बळीराम हेडगेवार, 1889 - 1940), der 1925 den RSS gegründet hat, war ebenfalls Mitglied der Hindu Mahasabha.
Die Partei setzt sich ein für die Wiedervereinigung von Indien und Pakistan unter dem Namen "Akhand Hindustan" (Hindi: अखण्ड हिन्दुस्तान). Das Ziel ist "Hindu-rashtra" (Hindi: हिन्दू राष्ट्र) also eine nationale Heimat für die Hindus bzw. eine nationale Heimat für die Hindus auf der ganzen Welt [s. Hindu Mahasabha vision & mission: http://www.abhm.org.in/about.aspx# -- Zugriff am 2017-11-17]
Als Folge der Ermordung von Mahatma Gandhi (Gujarati: મોહનદાસ કરમચંદ ગાંધી, 1869 - 1948) wurde Hindu Mahasabha zusammen mit dem RSS vorübergehend verboten. Der Mörder von Gandhi, Nathuram Godse (Marathi: नथूराम गोडसे, 1910 - 1949), war wohl Mitglied im Hindu Mahasabha, er hat sich eine Woche vor dem Mord im Büro von Hindu Mahasabha in Gwalior´s (Hindi: ग्वालियर) Daulatgunj (Hindi: दौलत गंज) aufgehalten. An der Stelle dieses Büros wird jetzt ein Tempel für den Mörder gebaut. Hindu Mahasabha-Anhänger wollten schon länger einen Tempel zur Erinnerung an Godse bauen, haben aber vom Staat Madhya Pradesh (Hindi: मध्य प्रदेश) kein Land für einen solchen Tempel bekommen. [s. Hindu Mahasabha lays foundation stone for temple to Gandhi´s killer Nathuram Godse : a temple to an assassin. - Huffpost. - 2017-11-16. - In: http://www.huffingtonpost.in/2017/11/15/hindu-mahasabha-lays-foundation-stone-for-temple-to-gandhis-killer-nathuram-godse_a_23279073/?utm_hp_ref=in-homepage -- Zugriff am 2017-11-17] Seit 2014 installiert Hindu Mahasabha Statuen, die Godse darstellen, in Tempeln in ganz Indien. Das Ziel ist, dass der Mörder Gandhis in die Götterwelt aufgenommen wird. Das ist z.B. mit Narad muni (Sanskrit: नारदमुनि), einem Weisen in den Puranas, passiert: für den RSS ist dieser der erste Reporter des Universums, der mit Pujas (Sanskrit: पूजा), Fasten, Gebeten, Seminaren usw. gefeiert werden muss. [s. Datta, Damayanti: Nathuram Godse, Narad muni. - 2017-09-28. - In: India today. - http://indiatoday.intoday.in/story/indians-invent-gods-and-goddesses-here-comes-the-new-gods/1/1057580.html-- Zugriff am 2017-11-22]

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Hindu Janajagruti Samiti [HJS] -- Hindi: हिन्दू जनजागृति समिति - एच जे एस |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 2002 |
| Hauptquartier | Goa (Konkani: गोंय) |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
https://www.hindujagruti.org/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCQGgsbqh-MwJCE7_hZFDL9g. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 https://www.facebook.com/hindujagruti/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hindu_Janajagruti_Samiti. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
Hindu Janajagruti Samiti [HJS] (Hindi: हिन्दू जनजागृति समिति - एच जे एस):
Die Organisation will die Hindus auf der ganzen Welt vereinen und eine Hindu-Nation errichten. Sie wurde 2002 gegründet
"for Education of Dharma, Awakening of Dharma, Protection of the Nation and Uniting Hindus" [s. Homepage].
Die Tätigkeiten der Organisation sind:
Kampf gegen
Die Darstellung dieser Themen auf der Homepage zeigen, dass die Organisation rechtsextrem und nationalistisch ist und aufhetzt. Zur Kommunikation werden täglich SMS an 300 000 Hindus geschickt. U.a. werden regelmäßig Treffen "All India Hindu Convention" abgehalten. Das 6. Treffen fand im Juni 2017 in Ramnathi (Konkani: रामनाथी) in Goa (गोंय) statt; die über 342 Delegierten aus 132 rechts gerichteten Organisationen kamen aus Indien, Nepal, Bangladesh und Sri Lanka. Sie fassten am 18.6.2017 eine Resolution mit der Forderung, dass Indien und Nepal zu Hindu Rashtra (Sanskrit: हिंदूराष्ट्र) erklärt werden. [vgl. Panaji: Declare India a 'Hindu Rashtra'. - In: Hindustan Times. - Kindle ed. - 2017-06-19]

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Hindu Vidhidnya Parishad -- Hindi: हिन्दू विधिज्ञ परिषद |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "association of advocates who thrive to work for the cause of nation and Hindu Dharma" |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 2012 |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | Hindu Janajagruti Samiti [HJS] Hindi: हिन्दू जनजागृति समिति - एच जे एस |
| Webpräsenz | https://www.hindujagruti.org/hindu-vidhidnya-parishad/. -- Zugriff am 2018-06-21 |
| Wikipedia |
| Name | Akhil Bharatiya Akhara Parishad [ABAP] -- Hindi: अखिल भारतीय अखाड़ा परिषद |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | --- |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Akhil_Bharatiya_Akhara_Parishad. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
Akhil Bharatiya Akhara Parishad [ABAP] (Sanskrit: अखिल भारतीय अखाड़ा परिषद): Spitzenorganisation von Hindu Heiligen und Asketen (Sadhus), zu der 14 Unterorganisationen sog. Akharas (Sanskrit: अखाड़ा) gehören. Es handelt sich um eine der wichtigsten Organisationen unter den Hindus, arbeitete mit Vishva Hindu Parishad (VHP) zusammen und gehörte dadurch zum Kreis des Sangh Parivar. Da ABAP sich nicht an politischen Wahlen beteiligt, arbeitet die Organisation wegen der BJP nicht mehr mit VHP zusammen. ABAP unterstützt den Bau des Ram-Tempels in Ayodhya (अयोध्या) und ist mitverantwortlich für die Organisation der Kumbh Mela (Hindi: कुंभ मेला). [s. Akhil Bharatiya Akhara Parishad. - In: Wikipedia.en. - 2016-12-28: http://www.wow.com/wiki/Akhil_Bharatiya_Akhara_Parishad -- Zugriff am 25-06-2017]

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Hindu Samhati -- Bengali: হিন্দু সংহতি |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Präsident 2018 | 2008 |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | Kolkata (Bengali: কলকাতা) |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz |
http://hindusamhati.net/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 http://hindusamhatibangla.com/ -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 https://www.facebook.com/HinduSamhati/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
Hindu Samhati (Bengali: হিন্দু সংহতি):
Ist eine bengalische Hindutva-Organisation, die inzwischen auch in Assam (অসম) und Jharkhand (Hindi: झारखंड) vertreten ist. Tapan Ghosh (তপন ঘোষ), ein swayamsevak (Sanskrit: स्वयंसेवक) seit 1970 war bis 2007 in verschiedenen Organisationen des Sangh tätig, aus Protest gegen den bengalischen Flügel des Sangh gründete er 2008 Hindu Samhati. Ghosh bemüht sich um die Bildung einer "Hindu Defence Force", die gegen die islamische Aggression kämpfen soll. Im britischen Parlament - eingeladen von MP Bob Blackmann (1956 - ) - forderte er dazu die Regierungen in Europa und den USA auf, auch soll die UN die Geburtenrate der Muslime einschränken. Er behauptet u.a., dass britische muslimische Pädophile eine Million weißer Kinder missbraucht hätten, und er lobt den Genozid an den Rohingya Muslimen in Myanmar. Ghosh hat Kontakte zu der extrem-rechten English Defence League. [s. Bhattacharya, Snigdhendu: Bengal-based Hindutva leader´s speech in British Parliament draws ire. - In: Hindustan times. http://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/bengal-based-hindutva-leader-s-speech-in-british-parliament-draws-ire/story-r2WAqo3Fhlaltkaj0MolCM.html - Zugriff 2017-10-29]
| Name | Karni Sena [Shri Rajput Karni Sena] (SRKS) -- Hindi: श्री राजपूत करणी सेना - एसआरकेएस |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.shrirajputkarnisena.com/. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shri_Rajput_Karni_Sena. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
Karni Sena [Shri Rajput Karni Sena] (Hindi: श्री राजपूत करणी सेना - एसआरकेएस): eine Organisation der Kaste der Rajputen (Hindi: राजपूत).
Leiter: Lokendra Singh Kalvi (Hindi: लोकेंद्र सिंह काल्वी).
Die Gruppe bekämpft das Zeigen des Padmaavat Films (Hindi: पद्मावत) . Weil der Film trotz vieler Proteste seit Anfang 2018 gezeigt werden darf, organisiert Karni Sena in vielen Städten gewalttätige Proteste, Anzünden von Autos, Blockaden auf Straßen und von Zügen. Beispiel: am 24.1.2018 wurde ein Bus in Gurgaon (Hindi: गुड़गांव/गुरुग्राम) angegriffen, der Schulkinder und ihre Lehrer transportierte. In Haryana (हरियाणा) wurde ein öffentlicher Bus angezündet und den Fahrgästen nur wenige Minuten gelassen, aus dem Bus zu springen, wobei die Staatspolizei zuschaute. In Pune (Marathi: पुणे) wurden zusammen mit weiteren Hindutva-Organisationen wie Bajrang Dal und Hindu Janajagruti Samiti Lastwagen angegriffen, Ticketschalter verwüstet, Kinos bedroht. [s. Chatterjee, Rituparna: The many ironies of Karni Sena´s destructive Campaign against 'Padmaavat'. - 2018-01-25. - In: Huffpost India http://www.huffingtonpost.in/rituparna-chatterjee/the-many-ironies-of-karni-senas-destructive-campaign-against-padmaavat_a_23342997/?utm_hp_ref=in-homepage -- Zugriff am 2018-02-02]

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Sanatan Sanstha -- Marathi: सनातन संस्था |
|---|---|
| Funktion | "Understand the science of Spirituality, do spiritual practice and attain Bliss" |
| Präsident 2018 | Jayant Balaji Athavale -- Marathi: जयंत बाळाजी आठवले (1942 - ) |
| Gegründet | 1999-03-24 durch Jayant Balaji Athavale (1942 - ) |
| Hauptquartier | Ramnathi, Goa (Konkani: गोंय) |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | https://www.sanatan.org/en/. -- Zugriff am 2018-06-21 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sanatan_Sanstha. -- Zugriff am 2018-06-21 |

Abb.: ©Logo
[Fair use]
| Name | Hindu Yuva Vahini [HJV] -- Hindi: हिन्दू युवा वाहिनी |
|---|---|
| Funktion | Yogi Adityanaths (योगी आदित्यनाथ, 1972 - ) Organisation zum Kampf für eine Hindu Nation gegen Minderheiten in Indien |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 2002 |
| Hauptquartier | Gorakhpur (Hindi: गोरखपुर) |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | http://www.hinduyuvavahini.in -- Zugriff am 2017-06-24
(in Hindi) https://www.facebook.com/search/top/?q=Hindu+Yuva+Vahini&init=public. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hindu_Yuva_Vahini. -- Zugriff am 2018-02-22 |
Yogi Adityanath (योगी आदित्यनाथ, 1972 - ) gründete die Organisation 2002 zwei Monate nach Beginn der Gujarat (ગુજરાત)-Pogrome. [Weitere Beteiligung der Organisation an Gewalttaten gegen Muslime s. 6. Adityanath.] Seit der Regierungsübernahme von Yogi Adityanath in Uttar Pradesh (उत्तर प्रदेश) hat die Organisation viele neue Mitglieder im ganzen Bundesstaat bekommen. Die Mitglieder gehen davon aus, dass jetzt sie das Gesetz sind. Da sie keine Hemmung haben, Menschen zu ermorden, fürchtet sich die muslimische Minderheit (20 % der Bevölkerung in Uttar Pradesh (उत्तर प्रदेश)]. Eine HYV-Whatsapp-Gruppe meldet sich bei den Mitgliedern, sobald sie den Verdacht hat, jemand könnte gegen die Hindutva-Ideologie sein.
Die Gruppe greift z.B. ein, wenn ein Fall von "Liebes-Dschihad" vorliegen könnte. Wollen ein Muslim-Junge und ein Hindu-Mädchen heiraten, wird davon ausgegangen, dass das Vorhaben von muslimischer Seite strategisch geplant ist, um das Hindu-Mädchen zum Islam zu bekehren. Damit so etwas von vorneherein abgeblockt wird, war eine der ersten Regierungstaten von Yogi Adityanath 64 Sonderheiten der Polizei zu bilden - sogenannte "Anti-Romeo-Einheiten", deren offizielle Aufgabe Schutz der Frauen vor sexuellen Übergriffen sein sollte, von korrupten Polizisten und verbrecherischen Gruppen aber inzwischen zur Erpressung genutzt wird. Von Mitgliedern der Hindu Yuva Vahini wird das genutzt, um vor allem die muslimische Minderheit zu unterdrücken.
So wurde z. B. am 9. Mai 2017 in Bulandshahr (बुलन्दशहर) (UP) der Nachbar einer Familie, deren Sohn mit einem Hindu-Mädchen verschwunden war, von Mitgliedern des HYV als Helfer der Flucht der beiden bezeichnet und ermordet. [s. Kant, Krishna : Ghulam Ahmed was lynched in Bulandshahr for the 'crime' of assisting an inter-religious couple to elope - an allegation his son denies. - In: The Wire. - 2017-05-09. - https://thewire.in/133915/hindu-yuva-vahini-ghulam-ahmed/ -- Zugriff am 2017-06-24]
Sehr wichtig ist für die Gruppe der Schutz der Kuh. Yogi Adityanath hatte nach seine Amtsübernahme sofort alle "nicht-lizensierte" Schlachthäuser für Büffel und Kühe schließen lassen. Dank der Informaten des HJV wurden daraufhin innerhalb von 24 Stunden 45 000 kleine meist muslimische Fleischläden geschlossen, wobei auch Geschäfte verbrannt wurden. [s. Germund, Willi : Miliz gegen "Liebesdschihad" : im Bundesstaat Uttar Pradesh (उत्तर प्रदेश) bedrohen Hindunationalisten die muslimische Minderheit; der Ministerpräsident stützt sich auf die Moped-Gang, die er mitgründete. - In: Frankfurter Rundschau. - E-Paper. - 2017-04-21. -http://www.fr.de/politik/indien-miliz-gegen-liebesdschihad-a-1264379 -- Zugriff am 2017-06-24.]
Da die Taten des HYV für die nächsten Wahlen für Yogi Adityanath ungünstig sein könnten, versucht z.B. Nagendra Singh Tomar (Hindi: नरेन्द्र सिंह तोमर, 1957 - ), der HYV-Staats-Sekretär, dass die Gruppe nicht mehr selbst Gewalt ausüben soll, denn man könne der jetzigen Regierung im Gegensatz zu den Vorgänger-Regierungen vertrauen, dass Meldungen von der Polizei verfolgt würden. Man soll diejenigen (nämlich Christen und Muslime), die Hindus bedrohen nicht mehr töten, sondern durch die Einheit der Hindus besiegen.
Hindu Yuva Vahini ist gegen das Kastensystem, weil sich die Hindus dadurch nicht genügend gegen die Aggression der Muslime wehren können. Man organisiert Treffen, bei denen verschiedene Kasten miteinander essen. Es gibt sogar Vorschläge für eine Kampagne, in der die Hindus aufgefordert werden sollen, ihren Familiennamen zu unterdrücken, denn dadurch kann man die Kaste erkennen. [s. Sharma, Betwa : With Boss Yogi as CM, Híndu Yuva Vahini is hawking a savvier shade of Hindutva. - In: HuffPost India. - 2017-04-27. - http://www.kractivist.org/with-boss-yogi-as-cm-hindu-yuva-vahini-is-hawking-a-savvier-shade-of-hindutva/ -- Zugriff am 2017-06-24.]
"Adityanath also prepared a work schedule for HYV leaders to follow strictly through the year.
- From mid- January to mid-February, they were supposed to mingle with members of the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes by organizing a sahbhoj [Hindi: सहभोज] (common feast) in their localities.
- From mid-February to mid-March, they were to conduct a membership drive.
- Then, until the end of May, they had to organize public meetings and rallies.
- For the rest of the year, the HYV’s state office-bearers visited different districts and concentrated on organizational work."
[Quelle: Jha, Dhirendra K.: Shadow armies : fringe organizations and foot soldiers of Hindutva. -- New Delhi : Juggernaut, 2017. --229 S. -- ISBN 978-93-8622-824-6. -- S. 45. -- Fair use]
| Name | Sri Ram Sene -- Marathi: श्रीराम सेने |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Präsident 2018 | Pramod Muthalik -- Kannada: ಪ್ರಮೋದ ಮುತಾಲಿಕ (1963 - ) |
| Gegründet | 2006 (!) |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sri_Ram_Sena. -- Zugriff am 2018-06-21 (Dort teilweise mit Sri Ram Sena verwechselt) |
| Name | Abhinav Bharat -- Marathi: अभिनव भारत |
|---|---|
| Funktion | |
| Präsident 2018 | |
| Gegründet | 2006-06 (?) durch Ramesh Upadhyay (Marathi: रमेश उपाध्याय) und Prasad Shrikant Purohit (Marathi: रसाद श्रीकांत पुरोहित) |
| Hauptquartier | |
| Mutterorganisation | |
| Webpräsenz | |
| Wikipedia | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abhinav_Bharat. -- Zugriff am 2018-06-21 |
"Even though the outcome of the investigation hangs in the balance, its nature and scope were unprecedented.The transcript of the set of meetings held by the members of the Abhinav Bharat over 2007 and 2008 is explosive. The proceedings were recorded by one of the participants (Sudhakar Dwivedi alias Amritananda Dev Tirth) on his laptop, and they provide us a glimpse of the Hindu Rashtra that is the ultimate goal of the Abhinav Bharat. The conversations, which are part of the charge sheet of the 2008 Malegaon blast case, delve into various issues ranging from a new Constitution and a new flag for the proposed Hindu Rashtra, to the justification of bomb blasts and the Abhinav Bharat’s cordial relations with the RSS and the BJR Here is an excerpt from one of them:
LIEUTENANT COLONEL PUROHIT: We will fight the Constitution, will fight the nation; this Constitution is not ours. [...] The only way is to knock it down [...]
SUDHAKAR DWIVEDI: On the first page of the Constitution it is written that the People of India have adopted this Constitution. How did this happen? On what basis could people adopt the Constitution? Was there any referendum? No. Was there any debate on it? No. How could then it be passed? How was this written on behalf of the people and who wrote it? [...]
PUROHIT: Swami ji, if this is so then we have to fight the Constitution; we have to fight for our independence.
SUDHAKAR DWIVEDI: We have an ancient science of administration. Our Smritis are the Constitution of our society. At present there are as many as 14 Smritis in this country. Collect them together [...]
PUROHIT: In this country we want to have Hindu Dharma or Vedic Dharma based on the Principles of Vedas.
MAJ. (RETD.) RAMESH UPADHYAY: This Constitution is not applicable to us, will not be acceptable to us; another Constitution will come into place; then Hindu Rashtra is established.
But a new Constitution based on the smritis was not considered sufficient for the new Hindu Rashtra. The key architect of the Abhinav Bharat also proposed a redesign of the tricolour:
‘The flag shall be solo tamed saffron flag having a golden border and an ancient golden torch. Length of the flag [shall] be twice its width [...] There will be four flames in four directions on that saffron flag representing [four] Vedas.
In order to establish the Abhinav Bharat as the conscience-keeper of the new nation, the transcript shows Purohit arguing that
‘wherever Abhinav Bharat is started, there should be a temple, the temple of Bharat Mata [...] That would give sanctity to the idea of nationhood.’
[...]
Clearly, establishing a Hindu Rashtra and taking revenge on Indian Muslims for ‘past acts of terrorism’ were not the only factors driving the Abhinav Bharat. Rakesh Dhawade, for instance, was doing all this for the sake of money. The charge sheet points out that many of the others were also working for pecuniary gains:
This Organised Crime Syndicate of Rakesh Dhawade were committing bomb blast since year 2003. The present accused have joined the said Organised Crime Syndicate and have continued their unlawful activities for their advantage [...] They have created an impression that they are taking revenge of bomb blasts committed by the alleged culprits belonging to Muslim community. The pecuniary gains of the members of this Organised Crime Syndicate are explained above by way of collection of funds and distribution of the same to the members of the organized crime syndicate for various purposes."
[Quelle: Jha, Dhirendra K.: Shadow armies : fringe organizations and foot soldiers of Hindutva. -- New Delhi : Juggernaut, 2017. --229 S. -- ISBN 978-93-8622-824-6. -- S. 148 - 152. -- Fair use]