

Zitierweise / cite as:
Carakasaṃhitā: Ausgewählte Texte aus der Carakasaṃhitā / übersetzt und erläutert von Alois Payer <1944 - >. -- Anhang A: Pflanzenbeschreibungen. -- Pongamia pinnata (L.) Merr. -- Fassung vom 2007-06-29. -- URL: http://www.payer.de/ayurveda/pflanzen/pongamia_pinnata.htm
Erstmals publiziert: 2007-03-19
Überarbeitungen: 2007-06-29 [Ergänzungen]; 2007-05-10 [Ergänzungen]; 2007-05-07 [Ergänzungen]
Anlass: Lehrveranstaltung SS 2007
©opyright: Dieser Text steht der Allgemeinheit zur Verfügung. Eine Verwertung in Publikationen, die über übliche Zitate hinausgeht, bedarf der ausdrücklichen Genehmigung des Verfassers
Dieser Text ist Teil der Abteilung Sanskrit von Tüpfli's Global Village Library
WARNUNG: dies ist der Versuch einer
Übersetzung und Interpretation eines altindischen Textes. Es ist keine
medizinische Anleitung. Vor dem Gebrauch aller hier genannten Heilmittel wird
darum ausdrücklich gewarnt. Nur ein erfahrener, gut ausgebildeter ayurvedischer
Arzt kann Verschreibungen und Behandlungen machen!
Falls Sie die diakritischen Zeichen nicht dargestellt bekommen, installieren Sie eine Schrift mit Diakritika wie z.B. Tahoma.
Verwendete und zitierte Werke siehe: http://www.payer.de/ayurveda/caraka0001.htm
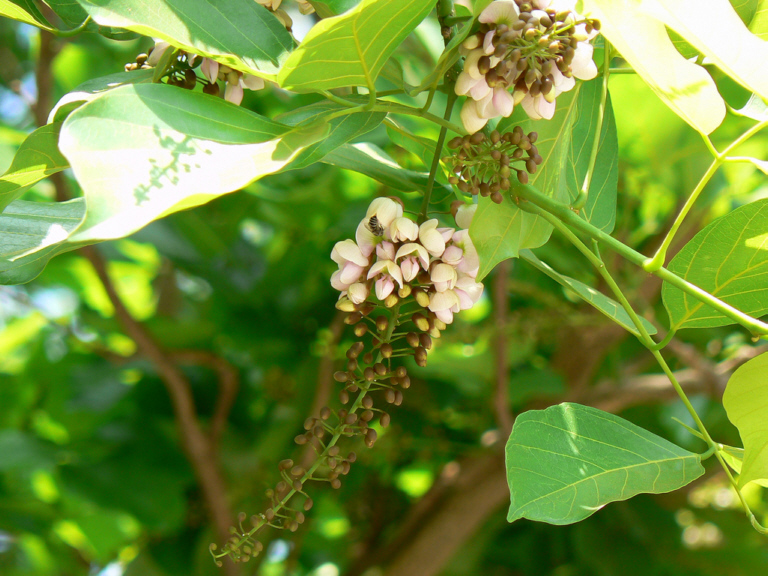

Abb.: Pongamia pinnata (L.) Merr.
[Bildquelle:
dinesh_valke. --
http://www.flickr.com/photos/dinesh_valke/470291271/. -- Zugriff am
2007-06-29. --
![]()
![]()
![]() Creative
Commons Lizenz (Namensnennung, keine kommerzielle Nutzung, keine
Bearbeitung)]
Creative
Commons Lizenz (Namensnennung, keine kommerzielle Nutzung, keine
Bearbeitung)]
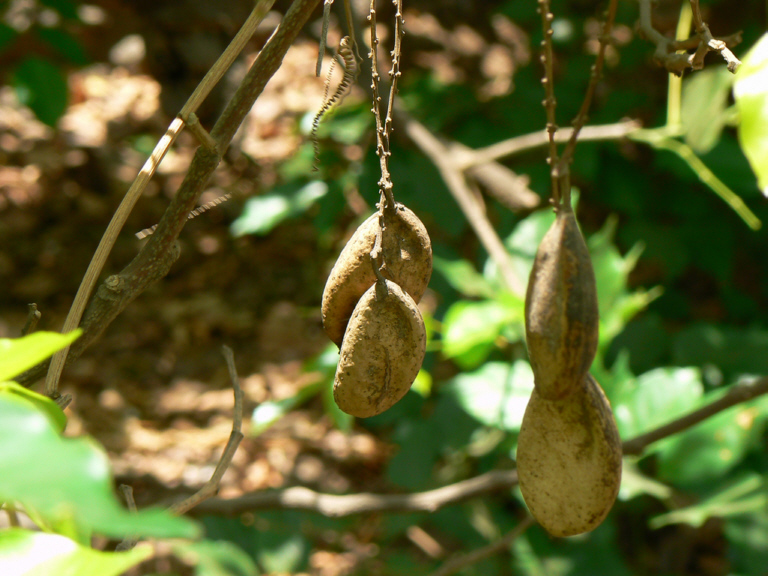

Abb.: Pongamia pinnata (L.) Merr.
[Bildquelle:
dinesh_valke. --
http://www.flickr.com/photos/dinesh_valke/470928930/. -- Zugriff am
2007-06-29. --
![]()
![]()
![]() Creative
Commons Lizenz (Namensnennung, keine kommerzielle Nutzung, keine
Bearbeitung)]
Creative
Commons Lizenz (Namensnennung, keine kommerzielle Nutzung, keine
Bearbeitung)]
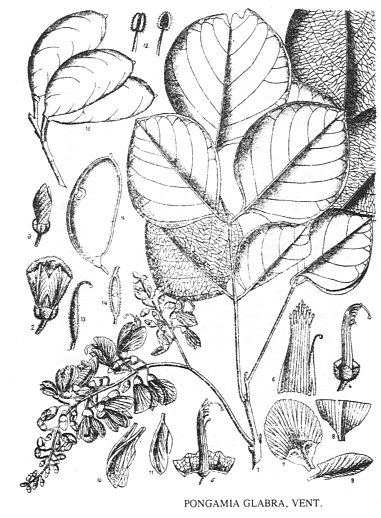
Abb.: Pongamia pinnata (L.) Merr.
[Bildquelle: Kirtikar-Basu, ©1918]
Drury:
"Pongamia glabra (Vent.) N. O. Leguminosae. Indian Beech, Eng. Pongam, Mal. Poongu marum, Tam. Kanoogoo, Tel. Kurung, Hind. Kurunja, Beng.
Description.—Tree ; leaves unequally pinnated ; leaflets opposite, 2-3 pairs, ovate, acuminated, glabrous ; racemes axillary, many - flowered, about half the length of the leaves ; pedicels in pairs ; vexillum with 2 callosities at the base of the limb and decurrent along the claw; legume oblong, nearly sessile, thick and somewhat woody, with a short recurved beak tumid along both sutures; calyx cup-shaped, red ; corolla papilionaceous, white. Fl. April—May. —W.& A. Prod. i. 262.—Wight Icon. t. 59.—Robinia mitis, Linn.—Dalbergia arborea, Willd.—Rheede, vi. t. 3.——Coromandel. Concans. Travancore. Bengal.
Medical Uses.—The seeds yield by expression a fixed oil, which the natives use externally in eruptive diseases.—(Roxb.) It holds a high place as an application in scabies, herpes, and other cutaneous diseases. Dr Gibson asserts that he knows no article of the vegetable kingdom possessed of more marked properties in such cases than the above. The oil is much used as an embrocation in rheumatism. Dr Crosse (Journ. Agri.-Hort. Soc., 1858, x. pt. ii. p. 223) has. made some valuable remarks on the physical characters and properties of this oil.—Pharm. of India.
Economic Uses.—The wood, which is light, white, and firm, is used for many economical purposes. The oil is used in lamps among the poorer classes. The leaves are eaten by cattle, and are valuable as a strong manure, especially for the sugar-cane.—Roxb."
[Quelle: Drury, Heber <1819 - 1872>: The useful plants of India : with notices of their chief value in commerce, medicine, and the arts. -- 2d ed. with additions and corrections. London : Allen, 1873. -- xvi, 512 p. ; 22 cm. -- s.v.]
Dutt:
"PONGAMIA GLABRA, Vent. Sans. Karañja, Nactamāla.
Vern. Darkaranja, Bang. Kiramāl, Hind.This tree appears to be common in, and well known all over India. The seeds are much used as an external application in skin diseases. The expressed oil of the seeds is used in these diseases as well as in rheumatism. A poultice of the leaves is applied to ulcers infested with worms. The seeds of Pongamia glabra, Cassia Tora (chakrumarda), and the root of Aplotaxis auriculata (kushtha), are rubbed into a paste with cow's urine, and applied to eruptive skin diseases.
Prithisāra taila.Take of the expressed oil of the seeds of Pongamia glabra one seer, kānjika eight tolās, roots of Plumbago Zeylanica (chitraka), Nerium odorum (karavira), Vitex Negundo (nirgundi), aconite, and the seeds of Gorchorus olitorius (nādika), eight tolās each, in the form of a paste made with kānjika. Mix them together and warm in the sun. This oil is said to be useful in various sorts of skin diseases, ulcers etc.
Tiktadya ghrita. Take of the leaves and fruits of Pongamia glabra, root of Picrorrhiza Kurroa, (katuki), wax, turmeric, liquorice root, leaves of Trichosanthes dioica (patala), Aganosma caryophyllata (mālati) and Azadirachta Indica (nim), equal parts, in all one seer. Beat them into a paste and boil with four seers of clarified butter and sixteen seers of water in the usual manner. This preparation is used as an ointment in unhealthy ulcerations and wounds."
[Quelle: Dutt, Uday Chand: The materia medica of the Hindus / Uday Chand Dutt. With a glossary of Indian plants by George King. -- 2. ed. with additions and alterations / by Binod Lall Sen & Ashutosh Sen. -- Calcutta, 1900. - XVIII, 356 S. -- S. 153.]