

Zitierweise / cite as:
Carakasaṃhitā: Ausgewählte Texte aus der Carakasaṃhitā / übersetzt und erläutert von Alois Payer <1944 - >. -- Anhang A: Pflanzenbeschreibungen. -- Solanum xanthocarpum Schrad. et Wendl. -- Fassung vom 2007-06-27. -- URL: http://www.payer.de/ayurveda/pflanzen/solanum_xanthocarpum.htm
Erstmals publiziert: 2007-06-27
Überarbeitungen:
Anlass: Lehrveranstaltung SS 2007
©opyright: Dieser Text steht der Allgemeinheit zur Verfügung. Eine Verwertung in Publikationen, die über übliche Zitate hinausgeht, bedarf der ausdrücklichen Genehmigung des Verfassers
Dieser Text ist Teil der Abteilung Sanskrit von Tüpfli's Global Village Library
WARNUNG: dies ist der Versuch einer
Übersetzung und Interpretation eines altindischen Textes. Es ist keine
medizinische Anleitung. Vor dem Gebrauch aller hier genannten Heilmittel wird
darum ausdrücklich gewarnt. Nur ein erfahrener, gut ausgebildeter ayurvedischer
Arzt kann Verschreibungen und Behandlungen machen!
Falls Sie die diakritischen Zeichen nicht dargestellt bekommen, installieren Sie eine Schrift mit Diakritika wie z.B. Tahoma.
Verwendete und zitierte Werke siehe: http://www.payer.de/ayurveda/caraka0001.htm
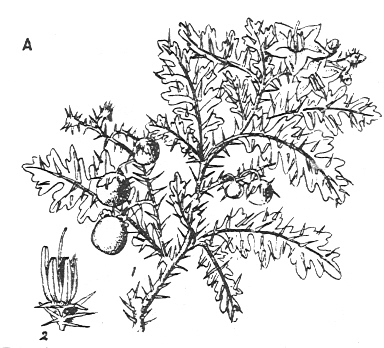
Abb.: Solanum xanthocarpum Schrad. et Wendl.
[Bildquelle: Kirtikar-Basu, ©1918]
Dutt:
"SOLANUM XANTHOCARPUM, VAR. JACQUINII, Schrad. Syn. Solanum Jacquinii, Linn.
Sans. Kantakāri, Nidigdhikā. Vern. Kantakāri, Beng. Kateli, Katai, Hind.
The root of Solanum Jacquinii is much esteemed as an expectorant and is used in cough, asthma, catarrhal fever and pain in the chest. It is an ingredient of dasamula ( see Desmodium gangeticum ), and is thus largely used in a great variety of diseases. The fruits are said to possess properties similar to those of the roots and are eaten as a vegetable.
Dr. W. C. Mookerjee, says " Kantakari is an invaluable medicine for Dropsy as a sequela of the advanced stage of Fever when all other modes of treatment fail. It is said by him to be a powerful diuretic and useful in chronic, violent and low fever, dropsy or general anasarca, low vitality of the general system, enlargement of liver and spleen. It is combined with kurchi in anasarca with Dysentery." Report of Dispensing, 1878.
Kantakāri is used in medicine in various forms, such as decoction, electuary, ghrita, etc. A decoction of the root is given with the addition of long pepper and honey, in cough and catarrh, and with rock salt and assafoetida in spasmodic cough. Several compound decoctions made along with other expectorant and demulcent drugs are in use. The following is an example. Take of kantakāri, root of Justicia Adhatoda ( vāsaka ), pulse of Dolichos uniflorus (kulattha ) and ginger, equal parts, in all two tolas; prepare a decoction in the usual way and administer, with the addition of pāchak root, in cough with difficult breathing.
Kantakāryavaleha or electuary of Solanum Jacquinii. Take of kantakāri root twelve seers and a half, water sixty-four seers, boil till reduced to one fourth and strain. Boil the strained decoction till reduced to the consistence of a fluid extract, and add to it the following substances in fine powder, namely, gulancha, Piper Chaba (chavya), plumbago root, tubers of Cyperus rotundus (mustaka), Rhus succedanea, ( karkata sringi), long pepper, black pepper, ginger, Alhagi Maurorum (yāsa), Clerodendron Siphonanthus (vārgi), Vanda Roxburghii, (rāsnā) and zedoary root, each eight tolas, sugar two seers and a half, sesamum oil and clarified butter each one seer, and boil together till reduced to the proper consistence. Lastly add honey one seer, bamboo-manna and long pepper in fine powder, each half a seer. This electuary is given in various sorts of cough.
Kantakāri ghrita. This is prepared in the usual proportions with the fresh juice of kantakāri, clarified butter and the following substances in the form of a paste, namely, Vanda Roxburghii ( rāsnā ), Sida cordifolia, ( balā ) ginger, long pepper, black pepper and the fruits of Tribulus terrestris (gokshura). It is used in the same cases as the electuary."
[Quelle: Dutt, Uday Chand: The materia medica of the Hindus / Uday Chand Dutt. With a glossary of Indian plants by George King. -- 2. ed. with additions and alterations / by Binod Lall Sen & Ashutosh Sen. -- Calcutta, 1900. - XVIII, 356 S. -- S. 208ff.]